Purpose
Understand the pathophysiology and the etiology of various coronary and cardiac vasculitis.
Show the potential of cardiac MDCT imaging to verify coronary and cardiac vasculitis on the basis of our cardiac MDCT registry with 45,
327 cases.
This exhibit aims to illustrate various imaging findings of coronary and cardiac vasculitis revealed by cardiac MDCT.
Methods and Materials
A.
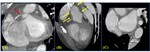
Coronary involvement of Takayasu’s arteritis ; 10-30% of Takayasu’s arteritis patient
• Type I : Stenosis or occlusion of the coronary ostia and the proximal segments of the coronary arteries (most common)[Fig.1 &2]
• Type II ; diffuse or focal coronary arteritis,
which can extend diffusely to all epicardial branches or can involve focal segments,
so-called skip lesions [Fig.3]
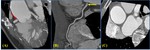
• Type III ; coronary aneurysm [Fig.4]
B.
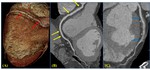
Cardiac sequalae of Kawasaki vasculitis [Fig.
5-8]
• Coronary artery dilatation,
premature atherosclerosis,
stenosis (4.7%),
thrombosis,
or...
Results
C.
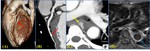
Cardiovascular involvement in Behçet’s disease [Fig.
9-10]
• Most common venous manifestation such as superficial thrombophlebitis
– Aneurysm ; thoracoabdominal aorta and branch vessels
– Occlusion ; less frequent than aneurysm,
late stage
– Pseudoaneurysms - on the aortic root,
aneurysm of coronary artery : extremely rare
– Venous thrombosis - deep and superficial vein and vena cava
• Cardiac involvement: 7~46%,
The incidence and nature is not yet clearly documented
• Aneurysm of sinus of Valsalva,
aortic or mitral valve involvement,
proximal aortic...
Conclusion
Although atherosclerosis is the most common cause of CADs,
there are various nonatherosclerotic causes of CADs
We can detect various causes of coronary and cardiac vasculitis as well as atherosclerotic lesion by cardiac MDCT.
Cardiac MDCT images are important for optimizing patent care in coronary and cardiac vasculitis.