Keywords:
Arteries / Aorta, Cardiac, CT, CT-Angiography, Diagnostic procedure, CAD, Education and training, Ischaemia / Infarction, Forensics
Authors:
K. Michaud, S. Grabherr; Lausanne/CH
Methods and Materials
Since 2009,
our center has investigated forensic cases by a standardized technique of PMCTA,
called multi-phase PMCTA (MPMCTA).
One of the main indications for this examination is suspicion of coronary artery pathology.
Radiological investigations
An unenhanced CT scan and subsequent y MPMCTA are performed before the classical autopsies following the standard protocol of MPMCTA (Fig 1).
A native CT-scan is performed prior to any manipulation of the body with an 8-row CT-unit (CT LightSpeed 8,
GE Healthcare,
Milwaukee,
WI,
USA).
Post-mortem liquid samples for toxicological screening and the analysis of cardiac biomarkers are collected using CT-guidance.
Unilateral femoral vessel cannulation is then performed under CT-guidance using cannulas (MAQUET Gmbh & Co.
KG,
Rastatt,
Germany) with a 16-French diameter for arteries and 18-French for veins.
A pressure-controlled perfusion device (Virtangio®,
Fumedica AG,
Maquet®,
Muri,
Switzerland) is used to inject a mixture of contrast agent (Angiofil®,
Fumedica AG,
Muri,
Switzerland) and paraffin oil.
Scan parameters are detailed in Table 1.
Autopsy and histological examination
A full classical autopsy including subsequent histological examination of selected tissue is performed for every case.
Autopsies are performed according to international recommendations for forensic pathology and cardiovascular pathology for sudden deaths suspected to be due to coronary artery disease.
Labeled segments of coronary arteries are collected and examined histologically.
Sampling of coronary arteries is guided by the results of the radiological and the macroscopic autopsy examination of the vessels.
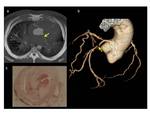
Radiological analysis of the coronary arteries is made on axial and reconstructed images.
As a detailed description of the radiological examination is generally available before autopsy,
the areas indicated as stenosis are already suspected before opening the body allowing the guidance of the macroscopic examination and sampling for histological examination.
The volume-rendered images are generally used to estimate the location of such regions of interest for the forensic pathologist.