Purpose
A number of previous studies have demonstrated the potential of 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) for non-invasive assessment of myocardial triglyceride (TG) content 1,2.
The improved availability of high field (3T) MR systems in clinical routine has facilitated more precise measurements of myocardial tissue metabolites,
as signal intensity is augmented according to field strength.
The use of double triggered (ECG- and respiratory motion gating) 1H-MRS enlarges the field of potential clinical application,
including cardiac examinations.
A strong correlation between in vivo (1H-MRS) and ex vivo myocardial...
Methods and Materials
Study population
Atotal of 40 healthy volunteers (22 males,
18 females; mean age ± standard deviation (SD) 31.9 ± 7.9 years for males vs.
31.6 ± 11.0 years for females) were included in this study and underwent cardiac MRI and 1H-MRS.
Cardiac imaging and spectroscopy
Double-triggered high-field cardiac MRI and 1H-MRS were performed using a 3 T magnet (MAGNETOM Trio®,
Siemens AG Healthcare Sector,
Erlangen,
Germany) equipped with a 12-channel phased array coil.
Subjects were scanned in supine position.
All participants underwent a fasting period...
Results
All participants of both genders successfully underwent morphological and spectroscopic imaging.
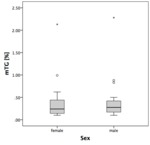
No significant difference of mTG between males (0.28%; IQR 0.17 - 0.42% [range 0.1 – 2.3%]) and females (0.24%; IQR 0.14 - 0.45% [range 0.1 – 2.1%]) was observed (Fig.
2) (p>0.05).
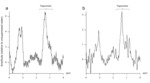
Figure 3 shows typical examples of myocardial 1H-MR spectra of a 22-year old male (Fig.
3a) and a 24-year old female (Fig.
3b).
Conclusion
Discussion
The present study used 1H-MRS at 3 T to determine potential gender related distribution differences of myocardial triglyceride content in healthy individuals.
Normal relative myocardial TG values,
as well as concentration ranges were assessed for both genders.
The method itself,
as well as the clinical application of 1H-MRS has made substantial progress throughout the last decade.
The benefits of respiratory navigator technique,
which significantly improves the reproducibility of in vivo myocardial TG determination,
were first described by Van der Meer et al.
in 2007...
References
1Reingold JS,
McGavock JM,
Kaka S,
et al.
Determination of triglyceride in the human myocardium by magnetic resonance spectroscopy: reproducibility and sensitivity of the method.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 289: E935–939.
2Den Hollander JA,
Evanochko WT,
Pohost GM.
Observation of cardiac lipids in humans by localized 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging.
Magn Reson Med 1994; 32: 175–180.
3O’Connor RD,
Xu J,
Ewald GA,
et al.
Intramyocardial triglyceride quantification by magnetic resonance spectroscopy: In vivo and ex vivo correlation in human subjects.
Magn Reson...