Purpose
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is chronic slowly developing condition caused by narrowing of vascular lumen with incidence strongly associated with increasing age.
A high quality CTA of the peripheral arteries may still be difficult due to wide scan range from lower abdomen to the forefoot and because of contrast timing issues,
especially if arterial occlusion or different flow patterns in left and right vasculature are present.
Therefore high contrast media (CM) volumes are still commonly used [2-4].
This study aimed to evaluate image quality of...
Methods and Materials
Population:
Between November 2015 and May 2016 there were 36 consecutive patients referred for evaluation of the peripheral arteries.
Contrast media protocol:
An uniform injection CM protocol was used.
A test bolus of 15 ml CM and 30 ml CM main bolus (Iopromide 300mgI/ml,
Ultravist,
Bayer; total iodine load was 13,5gI),
both followed by a 40 ml saline chaser were injected at 5ml/s injection rate with IDR 1,5gI/l.
Scan protocol:
Peripheral arteries were scanned on 3rd generation Dual Source CT scanner (Somatom FORCE,
Siemens Healthcare,...
Results
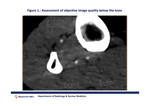
Objective IQ mean attenuation values and CNR (HU±SD) are listed in table in figure 2.
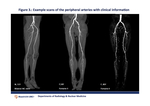
Subjective image quality median Likert scale assigned at the level of infrarenal aorta down to the popliteal segment was excellent.
In the calf,
median subjective IQ was rated as good.
(see figure 3.)
Conclusion
Adjusting low kV MDCT scanning protocols of the peripheral arteries individually to each patient according to the acquired bolus transit time allows to produce scans with sufficient image quality while reducing CM volume as low as 30ml.
References
Tendera,
M.,
et al.,
ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases.
European heart journal,
2011.
32(22): p.
2851-2906.
Qi,
L.,
et al.,
Image quality and radiation dose of lower extremity CT angiography using 70 kVp,
high pitch acquisition and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction.
PloS one,
2014.
9(6): p.
e99112.
Huang,
S.Y.,
et al.,
Assessment of vascular contrast and depiction of stenoses in abdominopelvic and lower extremity vasculature: comparison of dual-energy MDCT with digital subtraction angiography.
Academic radiology,
2012.
19(9): p.
1149-1157.
Almutairi,...