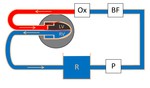
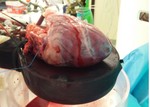
Purpose
Coronary artery disease (CAD) can be ruled out with high sensitivity and negative predictive value by using Computed tomography angiography (CTA).
However,
in case of an intermediate stenosis,
it is often difficult to determine hemodynamic significance,
reflected in the lower specificity and positive predictive value of CTA.(1) Therefore,
functional testing of hemodynamic significance is often required (2,
3).
Myocardial perfusion reduction is typically the first sign in the ischaemic cascade.
Quantification of myocardial perfusion defects could lead to faster and more accurate diagnosis of CAD....
Methods and Materials
The hearts of six Dutch landrace hybrid pigs were obtained from the slaughterhouse.
Protocols at the slaughterhouse and laboratory were in accordance with EC regulations 1069/2009 regarding the use of slaughterhouse animal material for diagnosis and research,
supervised by the Dutch Government (Dutch Ministry of Agriculture,
Nature and Food Quality),
and approved by the associated legal authorities of animal welfare (Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority).
In this study,
perfusion setup according to Langendorff was used (PhysioHeartÒ,
LifeTec Group,
Eindhoven,
The Netherlands) (14,15).
A centrifugal...
Results
All hearts recovered in stable sinus rhythm.
In one case,
a mechanical failure in the pressure wire prevented analysis of the pressure drop across the stenosis.
Therefore,
this heart was excluded from analysis.
In five of the six hearts,
all dynamic perfusion scans acquisitions were analysable.
There were no significant artefacts that influenced image evaluation.
During the five successful experiments,
arterial blood flow in the system ranged from 800 to 1210 mL/min with a mean value of 1021 mL/min and heart rate ranged from 83...
Conclusion
In an ex-vivo Langendorff porcine heart experiment,
differences in CT-derived myocardial perfusion parameters between ischaemic and non-ischaemic segments can be detected at stenosis grades with an FFR<0.80.
This model can be used in the systematic development and study of new imaging biomarkers for myocardial perfusion in a highly controllable and adjustable environment for CT.
Additional research in a clinical setting is required to translate the findings of this study into suitable cut-off values for quantitative CT perfusion parameters in patients with CAD.
References
1.
Hulten EA,
Carbonaro S,
Petrillo SP,
Mitchell JD,
Villines TC.
Prognostic value of cardiac computed tomography angiography: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Am Coll Cardiol.
2011 Mar 8;57(10):1237-47.
2.
Jaarsma C,
Leiner T,
Bekkers SC,
Crijns HJ,
Wildberger JE,
Nagel E,
et al.
Diagnostic performance of noninvasive myocardial perfusion imaging using single-photon emission computed tomography,
cardiac magnetic resonance,
and positron emission tomography imaging for the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis.
J Am Coll Cardiol.
2012 May 8;59(19):1719-28.
3.
Takx RA,...