Purpose
Cardiac magnetic resonance is the standard reference method for the assessment of left (LV) and right ventricular (RV) volumes, ejection fraction and mass. However, acquisitions are time-consuming and sometimes challenging to handle for patients suffering from heart condition. Accelerated techniques such as compressed sensing (CS)have been developed to decrease scan time1,2. CS is based on a random undersampling of a tranform image which is then restored by the use of iterative reconstructions3.Real-time compressed sensing cine (CSrt) has already been evaluated and is reliable for the...
Methods and Materials
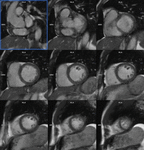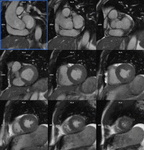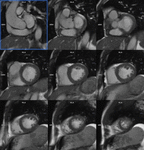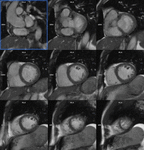
Thirty patients were enrolled. Each patient underwent (a) the reference retro-gated segmented steady-state free precession cine sequence (SSFPref), (b) the first generation real-time CSrt cine and (c) the segmented retro-gated prototype (CSrg) sequence providing the same number and positions of slices.
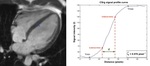
Image quality was assessed for the three sequences by using edge sharpness evaluation which is an estimate of the edge spread function. The latter is a robust and commonly used parameter in the field of objective and intrinsic image quality. Edge sharpness measurement method...
Results
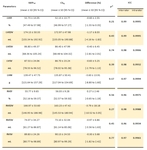
30 patients (22 males) were referred for: heart valve disease (n=9), ischemic cardiopathy (n=8), myocarditis (n=5), left ventricular hypertrophy (n=5) and infiltrative cardiomyopathy (n=3). Mean age was 48.0 ± 21.0 years-old. All patients could fully complete CSrt and CSrg breath-holdings.
Mean scan time was 485.4 ± 83.3 s (95 % CI: 454.3 to 516.5) using SSFPref. Regarding CS accelerated sequences, mean scan time was 23.9 ± 5.2 s (95 % CI: 21.9 to 25.8) with CSrt and 58.3 ± 15.1 s (95 % CI: 53.7...
Conclusion
CSrgimage quality is not different from the reference technique (SSFPref). The edge sharpness restauration provided by the segmented retro-gated evaluated sequence can be explained by the absence of interpolation since every frame of the cine images were actually sampled. Moreover, the two-heart-beats allows toreduce the partial k filling which improves sharpness too.
The prototype CSrg allows edge sharpness restauration and a reliable quantification of LV and RV volumes, ejection fractionand mass featuring a high acceleration factor and restores edge sharpness and image quality (Fig. 6,Fig....
References
1.Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007;58:1182–95.
2.Vincenti G, Monney P, Chaptinel J, et al. Compressed sensing single-breath-hold CMR for fast quantification of LV function, volumes, and mass. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014;7:882–92.
3.Donoho DL. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006;52:1289–306.
4.Vermersch M, Longère B, Coisne A, et al. Compressed sensing real-time cine imaging for assessment of ventricular function, volumes and mass in clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2019 [E-pub ahead of...