Purpose
Background
State-of-the-art mammography,
including digital mammography (DM),
is of pivotal importance to achieve early diagnosis of breast cancer,
and the only imaging tool proved to reduce mortality [1].
However,
the overlap of fibro-glandular tissue in dense breasts may affect sensitivity and specificity of DM by masking or mimicking a cancer [2].
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) is a novel imaging tool aimed to overcome tissue overlap,
since it is based on a moving x-ray source and a digital detector used to obtain a three-dimensional (3D) volume...
Methods and Materials
Patients
Over a 1-month period,
we prospectively obtained 22 consecutive surgical specimens (13 whole-breasts and 9 quadrants) from 22 patients (age range 41-82 years,
mean 62.0 years).
Patients were referred to surgery for biopsy-proven cancers in 21 cases and for one axillary nodal metastasis in 1 case with a CUP (Cancer of Unknown Primary) syndrome.
Pathologic examination of the specimen was used as the standard of reference.
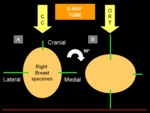
Imaging protocol
We sequentially performed DM and DBT by using the same digital system (Giotto TOMO,
IMS,
Bologna,...
Results
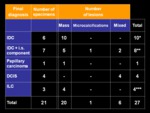
Final diagnosis
A total of twenty-seven lesions on 21 specimens were confirmed at pathologic examination.
Four specimens showed 2 lesions each,
whereas 1 specimen showed 3 lesions.
The remaining specimen from the patient with CUP syndrome was excluded from analysis,
since it showed no lesions at pathological examination.
An overview of lesions types and appearance on DM and/or DBT is shown in Table 1.
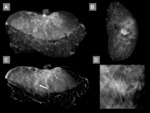
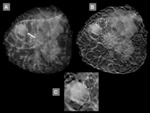
Diagnostic yield and agreement in measuring lesions size
DBT detected 27/27 lesions,
corresponding to a DY of 100% (95% C.I.
87.2-100),...
Conclusion
Limitations
Main study limitation is the small sample size.
However,
the collection of new cases is a work-in-progress in our Institution.
Additional results seem to confirm the trend we showed in this poster.
Conclusions
Regardless of lesion type (mass and/or microcalcifications),
DBT showed higher DY than DM by retrieving small lesions,
prevalently in dense specimens.
This is in accordance with previous results showing that DBT increases the sensitivity for cancer by reducing breast tissues overlapping [5-6].
DBT showed a reasonable agreement with DM in assessing...
References
Kolb TM,
Lichy J,
Newhouse JH.
Comparison of the performance of screening mammography,
physical examination,
and breast USand evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations.
Radiology 2002; 225(1): 165-75
Park JM,
Franken EA,
Garg M,
et al.
Breast Tomosynthesis: present considerations and future applications.
Radiographics 2007; 27:S231-S240
Lewin JM,
Niklason L.
Advanced applications of Digital Mammography: Tomosynthesis and contrast-enhanced Digital Mammography.
Semin Roentgenol 2007; 42(4):243-252
D'Orsi CJ,
Mendelson,
EB,
Ikeda DM,
et al: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System: ACR...
Personal Information
Thank you for the interest in this poster.
For any questions,
do not hesitate to contact me.
R.
Girometti
[email protected]
Aknowledgments
The Authors want to thank Dr.
Cristina Molinari for the revision of the manuscript.