This poster is published under an
open license. Please read the
disclaimer for further details.
Keywords:
Trauma, Tissue characterisation, Pathology, Comparative studies, Cone beam CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal bone, Extremities
Authors:
A. Vasiliev, N. Blinov, E. Egorova, D. V. Makarova, E. G. Gorlycheva; Moscow/RU
DOI:
10.1594/ecr2014/C-0705
Methods and materials
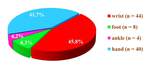
In total,
96 patients at the age from 24 to 65 years with posttraumatic changes and diseases of distal segments of upper and lower extremities were examined on modern CBCT-scanner – NewTom 5G (QR S.r.l.,
Italy) (Fig.
1).
Among all the examined patients 42,7 % (n = 41) of them were with posttraumatic changes,
57,3 % (n = 55) – with diseases of distal extremities.
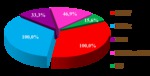
To assess diagnostic efficiency of CBCT,
its results were compared with the data of multislice computed tomography (MSCT) of patients with a similar pathology,
which was conducted on Brilliance 64 (Philips,
Netherlands) in 100,0 % (n = 96) cases.
In 33,3 % (n = 32) cases magnetic resonance tomography (MRI) of distal extremities was carried out on Centauri MPF 3000 (XinAO MDT,
China),
ultrasound examination (US) – on iU-22 (Philips,
Holland) in 15,6 % (n = 15) cases,
digital microfocus radiography (DMFR) was carried out on X-ray unit Pardus (Russia) and standard radiography (SR) of wrists,
hands,
feet and ankles to 46,9 % (n = 45) patients (Fig.
2).