Clinical Characteristics
The patients ranged in age from 1-12 years,
15 of the patients were females and 25 were males.
Of the 40 patients studied,
ten cases had chloroma as a primary presentation of the leukemia who had no systemic disease.
The other 30 patients had preexisting acute myeloid leukemia,
which was either in remission or in systemic bone marrow relapse at the time of presentation.
Seven patients had unifocal granulocytic sarcoma,
whereas the rest had multifocal disease.
Treatment included either chemotherapy,
radiotherapy,
or a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy,
with bone marrow transplantation.
Complete remission was achieved in five patients,
partial remission in three,
and no response in three.
Five patients experienced sequential extramedullary relapses (>1-year intervals),
arising at different sites.
Sites of Granulocytic Sarcoma
A total of 70 granulocytic sarcoma tumors were found in 40 patients over the 6 –year period.
The orbit,
intracranial and paranasal sinuses were the most common sites of granulocytic sarcoma.
Sites of orbital involvement (n = 17):- intraorbital extraconal masses (n = 12),
retro-ocular mass (n = 2),
perineural mass (n = 1),
intramuscular mass (n = 2).
Para nasal sinus involvement (n= 12).maxillary sinus affection is the commonest (n=7)
The intracranial involvement (n = 14): dural masses (n = 11),leptomeningeal ( n=1) and intra-axial mass (n = 2)
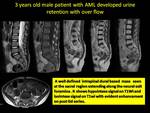
The intraspinal involvement (n = 5),
pure intraspinal mass (n = 3),
extension of paraspinal masses (n = 2),
The subcutenous choloroma (n = 3) ,
The liver (n = 3), focal lesion (n = 1),
periportal infiltration (n = 2),
The parotid region (n = 2),
skeletal muscles (n = 2),
the petrous region (n = 4),
abdominal cavity (n = 2), breast (n = 1),
kidneys ( n=2) pancreas (n=1) ,
testis ( n=1) and adenxa (n = 1).
Imaging Characteristics
Myeloid sarcoma generally presents as discrete soft tissue solid nodules or masses with variable enhancement.
Generally,
they were isodense to muscle on CT scans,
and isointense and hyperintense (mild to moderate) on T1- and T2wi,
respectively.
On US,
these lesions are usually iso to hypoechoic.
None of these lesions show internal calcification.
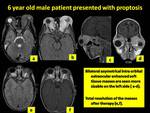
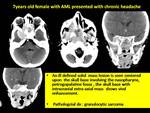
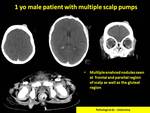
Orbital chlroma can affect any of its compartments : the extra conal mass with or without bony affection is the commonest location,
the extra ocular muscles,
lacrimal gland as well as the optic nerve can also affected,
the pattern of affection being bilateral and usually yet not always symmetrical can help in differentiation from other pediatrics orbital lesions ( Fig 1,2 ).
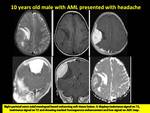
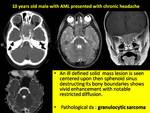
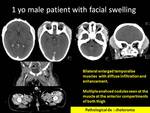
On MR imaging,
most of the intracranial chloroma are extra axial and they are usually iso to hypointse on T2WI with vivid uniform enhancement on post contrast series,
these lesions are hypercelluar so it usually shows restricted diffusion with reduced ADC value (Fig.
3).
This finding may help to differentiate such lesions from other meningeal lesions in the children.
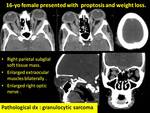
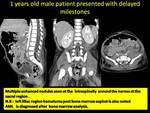
The affection of facial bone forming a mass involves the paranasal sinuses was one of the commonest encountered presentation of chloroma.
It may present with aggressive behavior destructing the bony boundaries extending intra orbitally and intracranially (Fig.
4,
5).
A spinal granulocytic sarcomas are either extension from para spinal mass (Fig.
6) or intraspinal extramedullary nodules (Fig.
7) both lesions enhanced markedly.
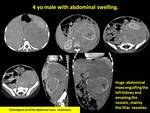
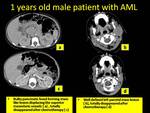
A huge abdominal mass with engulfment of the kidney are encountered in two cases of our patients,
and in both cases these lesions were the first presentation of the leukemia.
The lack of internal calcifications helps in differentiation between such lesions and the neuroblastoma,
and the encasement of the vessels help in differentiation of them from the masses of the renal origin (Fig.8).
The hepatic affection was noted in two pattern either periportal hypodense infiltration or focal lesions.
Breast and skin lesions were isodense to muscle on CT (Figs.9).
In the skin lesions,
moderate enhancement with and without rim enhancement was also noted.
In two patients,
muscle granulocytic sarcoma was multifocal and showed heterogeneous nhancement (Fig.
10).
Granulocytic sarcoma sited in the pancreas (Fig.
11),
lacrimal gland,
testes,
and kidneys tend to cause diffuse involvement rather than discrete masses.
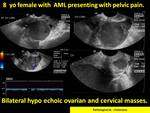
Female genital tract is a rare location of the granulocytic sarcoma,
heterogeneous hypoechoic adenxal mass lesion with low vascularity may raise the suspicious of hematological malignancy (Fig.
12).