This poster is published under an
open license. Please read the
disclaimer for further details.
Keywords:
Neuroradiology brain, CT-Angiography, MR, Thrombolysis, Acute
Authors:
J. A. Gadde, K. Anzilotti, X. Liu, A. Liu; Newark, DE/US
DOI:
10.1594/ecr2014/C-0897
Methods and materials
We retrospectively analyzed 95 consecutive patients with acute thrombus in the M1 or M2 segments of the middle cerebral artery.
All aspects of this retrospective study were approved by the institutional review board at our institution.
Inclusion criteria required each patient to be designated as a "Stroke Alert" or "Stroke Code" at our institution.
A Stroke Alert is defined as a patient who presents with a suspected acute stroke with sign/symptom onset within 4.5 hours and without a known contraindication to tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) or neurointerventional procedure.
A Stroke Code is defined as a patient who meets criteria for acute ischemic stroke with a decision made for revascularization with intravenous t-PA.
Each included patient must have received both a CT and CTA examination to be in the study.
The criteria also required each patient to have an MRI examination within approximately three days of the CT.
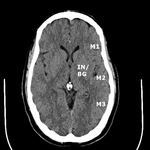
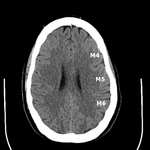
Collateral flow scores (CTACFS) for the middle cerebral artery territory via the ASPECTS vascular territories was independently assigned by two blinded neuroradiologists (Fig.
1-2).
The insula (IN) and basal ganglia (BG) were scored together for the purposes of this study.
The remaining M1 through M6 territories were separately evaluated.
The collateral scoring system was derived from a system originally designed for conventional angiograms (Tan et al 2007).
The collateral scoring system is as follows from a scale of 0 to 3: 0=absent collaterals,
1=collaterals less than or equal to 50% of the occluded territory,
2=collaterals greater than 50% but less than 100%,
3=100% collaterals.
The summation of these scores for the middle cerebral artery territory was calculated for each patient.
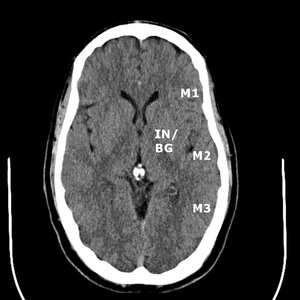
Fig. 1: ASPECTS territories for the middle cerebral artery distribution.
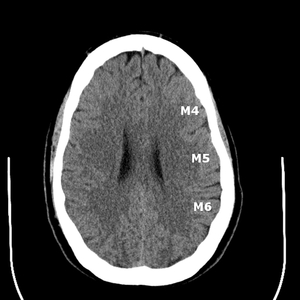
Fig. 2: ASPECTS territories for the middle cerebral artery distribution.
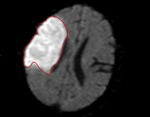
Total infarct volume was calculated by two independent radiologists via measurement and summation of all areas of restricted diffusion on the diffusion weighted sequence of the MRI (Fig.
3).
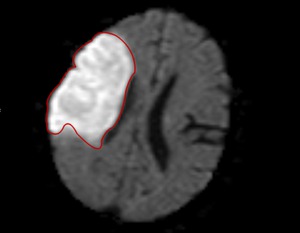
Fig. 3: Measurement of infarct volume using the diffusion weighted sequence of an MRI.
Statistical analysis
The interobserver agreement was calculated using the Cohen's K coefficient for the CTACFS.
The correlation of total CTACFS with total infarct volume and the correlation of CTACFS with NIHSS were calculated.
In those patients who underwent either thrombolysis and/or mechanical thrombectomy and had an NIHSS at both presentation and at discharge documented,
the difference was calculated and assessed for statistical significance.