Aims and objectives
The use of smartphone captured images for consultation is becoming increasingly popular due to improvement of the quality of the smartphone’s cameras and display screens.
In the recent years there has been major development of smartphones,
their applications,
screen resolution and camera’s image quality.
The development of multimedia applications and it is easy access through smartphones,
enabled physicians and healthcare workers to share clinical cases and data for academic or clinical purposes.
Some applications support end to end individual secure encrypted conversations which help secure...
Methods and materials
The study is a cross-sectional reliability study at the department of Radiology,
Sultan Qaboos University Hospital,
Oman.
The study included 15 patients who presented to the emergency department with acute lower quadrant pain and underwent CT scan of the abdomen to rule appendicitis.
The CT abdomen was done with intravenous and oral contrast.
The procedure notes and histopathology reports were traced to confirm the status of the appendix.
Six radiologist with different level of experience have participated as reviewers in the study.
Three reviewers were...
Results
Fifteen CT abdomen scans with IV and oral contrast of different patients were included in the study.
There were 7 normal appendices (6 normal,
1 not seen) and 8 abnormal appendices (5 inflamed and 3 inflamed with complications) that was confirmed using surgery notes and histopathology report.
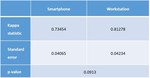
There was a strong agreement between reviewers in the smartphone reporting method (0.73) as well as in reporting workstation method (0.81).
The workstation method shows higher agreement rate between the reviewers compared to smartphone method (Table 1),
which...
Conclusion
The study showed that smartphone is reliable to diagnose acute appendicitis when considering a high quality video captured images from the work station.
References
1.
Drnasin I,
Grgic M.
The use of mobile phones in radiology.
In: Proceedings ELMAR-2010.; 2010:17-21.
2.
Rodrigues MA,
Visvanathan A,
Murchison JT,
et al.
Radiology smartphone applications; current provision and cautions.
Insights Imaging 2013;4:555-562.
3.
Bruikbaar S.
The free secure messaging app for medical team players.
Siilo 2018.
Available at: https://www.siilo.com.
Accessed October 1,
2018.
4.
Anon.
DocsInk.com | DocsInk.
Available at: https://docsink.com/.
Accessed September 17,
2017.
5.
Goost H,
Witten J,
Heck A,
et al.
Image and Diagnosis Quality of X-Ray Image Transmission...