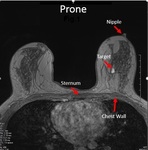
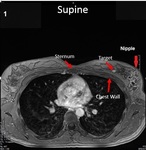
Aims and objectives
Targeted second-look ultrasound scan is frequently prescribed for patients with MRI-detected small breast lesions to increase MRI specificity or enable ultrasound guided biopsies and other procedures.
Despite its clinical relevance,
mapping MRI-detected small lesions that are obtained with the patient in prone position to their probable location while the patient is supine during an ultrasound scan,
remains a significant challenge due to the deformation of the breast.
Currently,
second-look ultrasound identifies 57.5% of MRI detected lesions at a pooled rate [1].
Many mapping methods have...
Methods and materials
Institutional review board approval was obtained from Marmara University Hospital,
Istanbul,
Turkey and all subjects signed the informed consent before data acquisition.
MRI images of 69 patients were obtained in prone and supine positions.
Standard clinical breast MRI images were acquired using a 3-Tesla scanner with the patient in prone position with a 16-channel phased-array dedicated breast coil.
Examination protocol included following sequences: (1) Axial turbo spin-echo fat saturated T2-weighted sequence (TR/TE 4100/70 ms,
field of view 30 cm,
acquisition matrix 440x380,
slice thickness 3...
Results
Our model predicting the target location in supine has reached a prediction accuracy of 14.2 +/-1.4 mm (mean+/- SD) for the median error and 16.3 +/-1.5 mm for the mean error (Figure 2).
Accuracy was calculated as the distance between the predicted and actual target location in the supine position.
To understand how the ML model determines supine target position,
we explored the importance of individual predicators by measuring their influence on the developed model.
The most important predictor of the target location in the...
Conclusion
Our ML-based model shows promise in predicting lesion location in supine position from prone MRI images with a mean error of <17mm,
which is likely to improve with adding more data sets and predictors.
Future inclusion of automated detection of landmarks will further expedite the calculation of the supine target predicted position.
The obtained results support the feasibility of using trained algorithms to predict the position of small prone MRI-detected breast lesions in supine position and provide guidance for supine breast ultrasound exams or other...
References
References:
1. Fausto A.
et al.
Six-year prospective evaluation of second-look US with volume navigation for MRI-detected additional breast lesions.
Eur Radiol.
2018 Oct 15
2. Martinez F et al.
A finite element-based machine learning approach for modeling the mechanical behavior of the breast tissues under compression in real-time.
Comput Biol Med.
2017 Nov 1;90:116-124
3. Zou,
H.
& Hastie,
T.
Regularization and Variable Selection via the Elastic Net.
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society.
Series B (Statistical Methodology) 67,
301-320 (2005).
4. Pedregosa et...