Learning objectives
- Identifying the normal sonographic appearance of the normal tonsil and providing a step by step tonsillar ultrasound (US) technique;
- Identifying some of the most frequent tonsillar findings;
- Recognizing ultrasound evaluation as an important diagnostic tool of peritonsillar swelling.
Background
Tonsillar/Peritonsillar infections include uncomplicated tonsillitis,
peritonsillar cellulitis,
intratonsillar abscess and peritonsillar abscess,
conditions with similar clinical presentations.
Peritonsillar abscess,
the most common deep space neck infection,
particularly in children and adolescents,
can have life-threatening complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly,
such as sudden rupture with aspiration,
extension of the infection into the mediastinum,
acute airway obstruction and/or sepsis.
The formation of an abscess usually begins as a superficial infection or acute tonsillitis that progresses to a peritonsillar cellulitis and further to a peritonsillar abscess....
Findings and procedure details
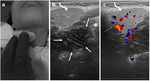
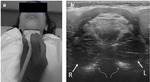
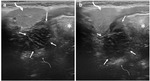
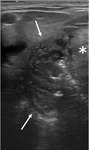
The ultrasonography (US) provides valuable information on peritonsillar swelling.
We will describe our ultrasound technique and present some illustrative images from clinical practice.
In our department,
we have been mainly using the transcutaneous ultrasound technique.
Why?
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of the neck traditionally has been used to accurately diagnose suspected peritonsillar abscess (PTA).
However,
it is far from ideal.
It is an expensive method,
and there is a growing concern over radiation exposure,
which can lead to an increase rate of cancer especially...
Conclusion
Ultrasonography is an accurate,
noninvasive and inexpensive tool that can play an important role in promptly diagnosing peritonsillar abscess which in turn is fundamental to adequately treat and improve the outcome.
Therefore,
radiologists must be familiar with the normal sonographic anatomy of the palatine tonsils and the spectrum of peritonsillar infections that may manifest as peritonsillar swelling.
However,
there are some clinical conditions in which performing computed tomography imaging may improve the reliability and accuracy in the final diagnosis.
References
1.
Bandarkar AN,
Adeyiga AO,
Fordham MT,
Preciado D,
Reilly BK.
Tonsil ultrasound: technical approach and spectrum of pediatric peritonsillar infections.
Pediatr Radiol.
2016 Jun;46(7):1059-67
2.
Buckley AR,
Moss EH,
Blokmanis A (1994) Diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess: value of intraoral sonography.
AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:961–964
3.
Ahmed K,
Jones AS,
Shah K et al (1994) The role of ultrasound in the management of peritonsillar abscess.
J Laryngol Otol 108:610–612
4.
Scott,
P.M.J.; Loftus,
W.K.; Kew,
J.; Ahuja,
A.; Yue,
V.; Van Hasselt,
C.A.
Diagnosis...