Purpose
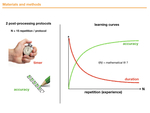
The learning curve was conceptualized and popularized in 1936 by the American aeronautical engineer, Theodore Paul Wright (1). Its first use was to estimate the consequences of the serial production of an aircraft on its unit cost, using a graphical representation of the cost as a function of the number of aircraft manufactured. The repetition of the same task by workers, improves their performance and leads to a reduction in time, effort and therefore cost per unit produced. However, a learning period is necessary to...
Methods and materials
This study was carried out on 21 radiographer students (17 women, 4 men, mean age: 21.3 years). These 3rd year students have already received all the theoretical training related to the post-processing protocols and have all accumulated at least 8 weeks of full-time internships in a CT department (Fig 2).
Each post-processing protocol was performed 15 times by each student over a 4-week period in the training centre (Fig 2 and Fig 3). The post-processing protocols were carried out on Horos software (v2.1.1) (horosproject.org) on...
Results
The learning rates for protocols #1 and #2 are 63% and 56% respectively according to the Wright correlation(Fig 6). In both protocols, the standard deviations decrease significantly and stabilize during rehearsals, which means that the rehearsals are effective.
The results concerning the progress of the accuracy of the work performed (Fig 7) are correlated (Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm) (10) with the following relation:
S = 1 - e-µ·N
with:
S = Score (between 0 and 1) of the Nth post-processing
N = the operation number (post-processing)
µ...
Conclusion
To our knowledge, this work is the first to focus on the use of learning curves for Radiographers students (Fig 7 and Fig 8). The combined analysis of the learning curves and the quality results shows that the group level became homogeneous and qualitative at the end of the study. These curves allow trainers and supervisors to more precisely qualify the learning difficulty of a task while motivating students. The use of these curves is perfectly in line with the competency-based training paradigm (11).
Personal information and conflict of interest
J.-P. Dillenseger; Strasbourg/FR - nothing to disclose C. Zorn; Strasbourg/FR - nothing to disclose P. Choquet; Strasbourg/FR - nothing to disclose E. Bauer; Strasbourg/FR - nothing to disclose G. Bierry; Strasbourg/FR - nothing to disclose
References
1. Taïeb, H., Russell, F., Brian, K. Le management stratégique: Synthèses et guides pour les managers. Editions JFD; 2019.
2. Wright, T.P. Factors Affecting the Cost of Airplanes. Journal of Aeronautical Sciences. 1936;3(4):122-28.
3. Yelle, L. E. The learning curve: Historical review and comprehensive survey. Decision sciences, 1979,10(2):302-328.
4. Berti, P., Raffaelli, M., Materazzi, G., et al. Parathyroïdectomie vidéoassistée: courbe d’apprentissage. In : Annales de chirurgie.126(8);772-776.
5. Dias, T.R., Alves Junior JDC, Abdala, N. Learning curve of radiology during training in fluoroscopy-guided facet joint injections....