Learning objectives
To recognize specific signs of small airway diseases on high resolution computed tomography scan (HRCT).
To assess the role of paired inspiratory and expiratory CT scans.
Role of different post processing Techniques like multiplanar reconstructions with maximum intensity projection (MIP) and minimum intensity projection (MinIP) in diagnosing small airway diseases.
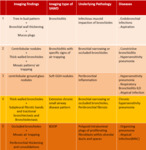
To provide an easy and schematic diagnostic approach in small airway diseases and propose an easy way to classify bronchiolitis.
Background
Introduction to Small airways and Bronchiolitis:
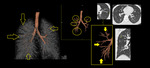
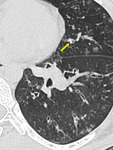
Small airways are bronchioles that do not contain cartilage and have an internal diameter of 1.These small airways are located between the fourth and the 14th generation of the tracheobronchial tree, are only visualized on CT images when diseased ( Fig. 1) and comprise the smallest air conducting membranous bronchioles and respiratory bronchioles, which open into the gas-exchange apparatus (the alveoli)2.
Bronchiolitis or small airway disease is a generic term used clinically to describe various inflammatory diseases of the...
Findings and procedure details
MDCT Technique for small airway diseases:
Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) scanners allow diagnosis and monitoring of lung disease at substantially lower radiation doses than with prior scanners.There are two types of CT scanning protocols currently used to assess lung disease:
(1) High-resolution CT (HRCT) imaging, in which thin 0.5–1.5-mm slices are obtained every 0.5, 1, or 2 cm from apex to base for inspiratory scans, and limited, spaced HRCT slices obtained for expiratory scans.
(2) Complete spiral CT imaging covering the entire lung for inspiratory...
Conclusion
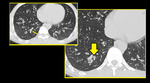
HRCT images can accurately identify thickened airway walls, plugged small airways and air trapping.HRCT plays instrumental role in characterization and detection of small airway diseases which, until relatively recently, had been regarded as being beyond the scope of radiological imaging.
HRCT images with mosaic attenuation areas should be paired with expiratory scans for early disease detection and to prevent irreversible lung damage.
The diagnosis of air trappingis more confidently made when the imagesare used in conjunction with expiratory images.
There is improvement in diagnosing mosaic...
Personal information and conflict of interest
Primary author:
Dr. Ummara Siddique Umer
MBBS (KEMC), FCPS (Radiology) , EDiR (EBR)
Consultant Radiologist & Assistant Professor of Radiology
Rehman Medical Institute Peshawar
Pakistan
Disclosure:
U. S. Umer; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
S. Alam; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
S. Gul; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
S. Ghulam Ghaus; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
A. Nawaz Khan; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
H. Abid; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
S. Iqbal; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose.
K. Nawab; Peshawar/PK - nothing to disclose....
References
Burgel PR, de Blic J, Chanez P. Update on the roles of distal airways in asthma. Eur Respir Rev 2009; 18: 80–95.
Burgel PR, Bergeron A, Blic JD, Bonniaud P, Bourdin A, Chanez P et al. Small airways diseases, excluding asthma and COPD: an overview. European Respiratory Review Jun 2013, 22 (128) 131-47.
Hogg JC. Pathophysiology of airflow limitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004; 364: 709–21.
Müller NL, Miller RR. Diseases of the bronchioles:CT and histopathologic findings.Radiology 1995.196:3-12.
Stone T, Reynolds JH, and...