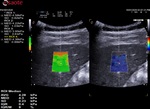
- Description of the technology Esaote QElaXto 2D to understand the information displayed during the stiffness assessment and the outcomes.
- Description of the practical and technical aspect of the method – regarding the patient position, the probe position, the field of view (FOV) stiffness box and the samples of measurements called region of interest (ROI).
- Description of the quality parameters.
Esaote QElaXto 2D Technology
QElaXto 2D is a SWE Technique from Esaote (S.p.A., Genoa, Italy).
QElaXto 2D, available on the ultrasound platform MyLab™9eXP, can provide quantitative liver stiffness assessments with the probe C1-8, a single crystal convex transducer.
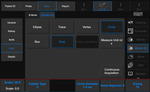
When QElaXto 2D is active, a dedicated menu is displayed on the touchscreen to facilitate the workflow and the acquisitions.
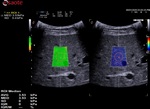
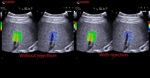
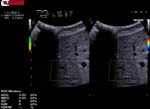
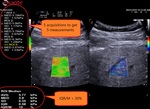
QElaXto 2D alternates multiple perturbations and reading phases, enabling an image of the stiffness for a small tissue sample.
The system creates several shocks side the box that will induce some shear waves. Then it tracks the radio frequency (RF) signal of the tissue displacement on multiple sample stripes inside the box and measures the shear waves velocity for each strip.
The velocity is, in a second time, associated to a color map and then QElaXto 2D codes each strip with color pixels in order to enable a colored representation of the stiffness in the sample.
Then the clinicians had to perform five valid measurements inside the box to get a quantitative assessment, placing the ROI in an area free from vessels, bile ducts and artefacts.
QelaXto 2D can provide the following measurements:
- - Average (AVG) in kPA or m/s
- - Median (MED) in kPa or m/s
- - Standard Deviation (SD) in kPpa or m/s
- - Interquartile Range (IQR) in kPa or m/s
- - IQR/MED in %
The user interface is optimized for productivity and is fully customizable to simplify the acquisitions.
- - The acquisitions can be continuous or one-shot
- - Possible automatic save-image after each measurement
- - Automatic export in the report at the end of each sessions
- - Dedicated report and worksheet
- - Intelligent algorithm to reject false measurements
- - Possibility to delete previous measurements in the current session
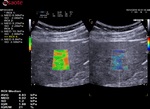
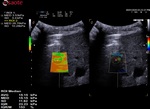
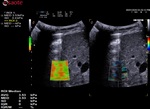
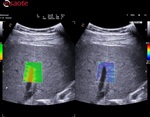
To help the clinicians in having reliable measurements, QElaXto 2D offers some further tools that are the dispersion map and the rejection parameter.
1. The dispersion map
The dispersion map is the computation of the standard deviation of the value of each pixel in comparison with the surrounding ones.
- Green means that the reliability is good
- Orange means that the reliability is weak
It can be enabled side the stiffness imaging in a dual mode visualisation.
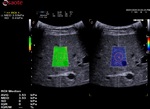
2. The rejection parameter
The rejection parameter indicates to the algorithm the rejection level for the artefacts, vessels and weak shear waves.
With rejection activated, the algorithm won’t include the pixels coming from the rejected areas in the computation of the values.
Acquisition procedure
a- Scanning Instructions
- Recommended fasting of 4-6 hours.
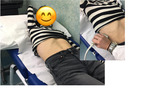
- Right intercostal access has to be used, with the patient in the dorsal decubitus position, examining the right lobe of the liver (VI/VII segments) by using the Convex array.
- Put the right arm of the patient behind his/her head in order to maximize the intercostal space, as it is shown in the figure 3 of this section.
- The coupling between probe and liver has to be complete (the whole echo image has to be properly visible) - a correct amount of gel has to be used. Dark areas of the echo image, reverberations artefacts and ribs shadows have to be avoided.
- Higher is the skin to liver distance lower will be the reliability of the measurements.
- A correct light pressure has to be applied, in order to be stable and to be properly coupled with the skin over the liver - the pressure shouldn’t be not excessive in order to not compress the liver.
- No respiration during the acquisition, the patient should be asked to stop breathing just for few seconds in neutral respiratory phase, without a deep inspiration.
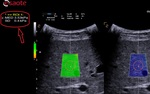
b- Box positioning
- The box has to be positioned in an area free of vessels, bile ducts or nodules.
- The box has to be positioned 1-2cm below the Glisson capsule to avoid reverberation artefacts. The optimized depth is not deeper than 4-5.
- The box has to be positioned in the orthogonal axis to the capsule.
a. c- Number of measurements
- According to the guidelines 5 valid measurements have to be obtained
- It is better if SD<30% for each evaluation
- The session (ended after 5 valid acquisitions) can be reliable when IQR/MED<30%
Descriptions of the quality parameters
- SD<30% of Med value
- IQR/M of the 5 measurements <30%
- Rejection parameter
- Dispersion map
- To position the ROI in the most reliable area. Indeed, the orange areas means that the reliability is low in case of artefacts, low coupling between the probe and the liver or even presence of vessels.
- To help the clinicians to get more reliable values in the liver assessment and to reduce the time of acquisition per session.
Pitfalls
- Low echogenicity and thick abdominal wall could make weak shear waves
- Modification of the acquisition liver window between the different acquisitions
- Box axis not perpendicular to the Glisson capsule
- Artefacts if not rejected could impact the values
- Liver stiffness value must be interpreted on the basis of clinical and laboratory data
- Some conditions can over-estimate the liver stiffness value: food intake, acute viral hepatitis, transaminases flares, congestive heart failure, extrahepatic cholestasis, infiltrative diseases