Learning objectives
To review the anatomy of the intracranial veins.
To enumerate the pathological conditions affecting these veins.
To demonstrate various conditions in which these intracranial veins are affected secondarily.
Background
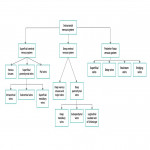
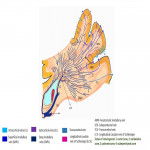
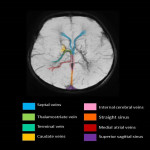
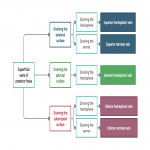
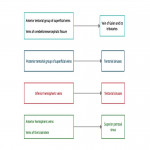
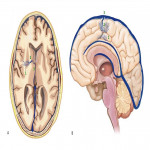
A. Relevant cerebral venous anatomy1 : The intracranial venous system is classified as the (1) superficial cerebral venous system, (2) deep cerebral venous system and (3) posterior fossa venous system (Fig 1,2)
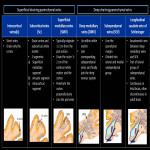
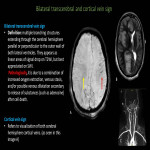
The superficial cerebral venous system: consists of venous sinuses along with pial veins and the superficial parenchymal veins. The pial and the superficial parenchymal veins drains most of the cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter. The superficial parenchymal veins namely the intracortical, subcortical and superficial medullary veins derive their respective names from their...
Findings and procedure details
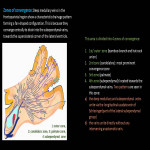
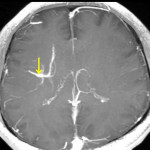
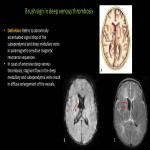
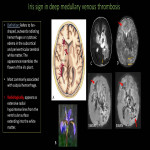
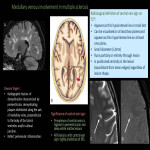
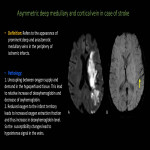
The deep medullary veins are affected in a number of pathological conditions, either primarily or secondarily. A typical feature of these pathologies is that they show a characteristic distribution indicating the relationship to the medullary vein. Here, we will enumerate those causes (Fig 11).
Structural anomalies of the medullary veins1
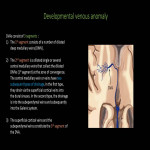
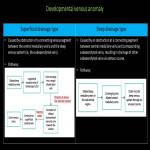
Developmental venous anomaly (DVA) (Fig 12-15)
Most common intracranial vascular malformation (55% of all vacular malformations).
Common locations: frontoparietal region(36-64%) and cerebellar hemisphere (14- 27%)
Imaging: On imaging, they appear as medusa-like, mushroom-shaped, or umbrella-shaped...
Conclusion
Understanding the structure, drainage pattern of the parenchymal veins play a major role in diagnosis of the pathologies related to these relatively unexplored vascular channels. Characteristic distribution of the lesions and typical appearance are instrumental in determining primary or secondary involvement of parenchymal veins and thus prompt diagnosis of a gamut of pathological conditions.
Personal information and conflict of interest
S. Mahal:
Nothing to disclose
S. Tiwari:
Nothing to disclose
T. Yadav:
Nothing to disclose
P. K. Garg:
Nothing to disclose
P. S. Khera:
Nothing to disclose
B. Sureka:
Nothing to disclose
References
Taoka T, Fukusumi A, Miyasaka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, Kichikawa K, et al. Structure of the medullary veins of the cerebral hemisphere and related disorders. Radiographics. 2017 Jan;37(1):281-97.
Matsushima T, Rhoton AL, de Oliveira E, Peace D. Microsurgical anatomy of the veins of the posterior fossa. Journal of neurosurgery. 1983 Jul 1;59(1):63-105.
Arrigoni F, Parazzini C, Righini A, Doneda C, Ramenghi LA, Lista G, et al. Deep medullary vein involvement in neonates with brain damage: an MR imaging study. American journal of neuroradiology. 2011...