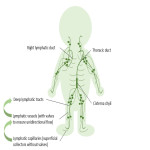
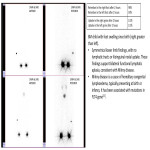
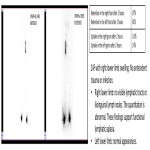
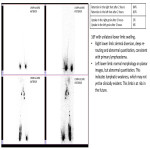
All images with thanks to Department of Radiology, St George’s University Hospital NHS Trust, London, UK 2023
[1] Lymphedema: Pathogenesis and Novel Therapies. Joseph H. Dayan, Catherine L. Ly, Raghu P. Kataru, Babak J. Mehrara. Annual Review of Medicine 2018 69:1, 263-276.
[2] Using Lymphoscintigraphy to Evaluate Suspected Lymphedema of the Extremities. Mariam Moshiri, Douglas S. Katz, Marvin Boris and Elizabeth Yung. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2002;178: 405-412.
[3] Primary Lymphedema: Clinical Features and Management in 138 Pediatric Patients. Schook, Carolyn C. B.A.; Mulliken, John B. M.D.; Fishman, Steven J. M.D.; Grant, Frederick D. M.D.; Zurakowski, David Ph.D.; Greene, Arin K. M.D., M.M.Sc. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 127(6):p 2419-2431, June 2011.
[4] Dynamic lymph flow imaging in lymphedema. Normal and abnormal patterns. K Nawaz, M M Hamad, S Sadek, M Awdeh, B Eklof, H M Abdel-Dayem. Clin Nucl Med. 1986 Sep;11(9):653-8.
[5] Lower-limb lymphatic drainage pathways and lymph nodes: a CT lymphangiography cadaver study. Akira Shinaoka , Seijiro Koshimune, Hiroo Suami, Kiyoshi Yamada, Kanae Kumagishi, John Boyages, Yoshihiro Kimata, Aiji Ohtsuka. Radiology. 2020 Jan;294(1):223-229. Epub 2019 Nov 19.
[6] Primary lymphoedema. Pascal Brouillard, Marlys H Witte, Robert P Erickson, Robert J Damstra, Corinne Becker, Isabelle Quéré, Miikka Vikkula. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Oct 21;7(1):77.
[7] Lymphoscintigraphy for Evaluation of Lymphedema Treatment: A Systematic Review. Forte AJ, Boczar D, Huayllani MT, Lu X, Ciudad P. Cureus. 2019 Dec 12;11(12):e6363.
[8] Role of lymphoscintigraphy in diagnosis and management of patients with leg swelling of unclear etiology. Tek Chand Kalawat, Ravi Kumar Chittoria, , Praveen Kumar Reddy, Batchu Suneetha, Ravishwar Narayan, Parthsarthi Ravi. Indian J Nucl Med. 2012 Oct-Dec; 27(4): 226–230.
[9] New clinical and laboratory staging systems to improve management of chronic lymphedema. Lee BB, Bergan JJ. Lymphology 2005;38:122‑9.
[10] Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Filarial Lymphedema and Its Management. R. K. Shenoy. Korean J Parasitol. 2008 Sep; 46(3): 119–125.
[11] The lymphatic phenotype in Noonan and Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome. Sarah Joyce, Kristiana Gordon, Glen Brice, Pia Ostergaard, Rani Nagaraja, John Short, Sandra Moore, Peter Mortimer, and Sahar Mansour. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 May; 24(5): 690–696.
[12] Analysis of the phenotypic abnormalities in lymphoedema-distichiasis syndrome in 74 patients with FOXC2 mutations or linkage to 16q24. G Brice, S Mansour, R Bell, J R O Collin, A H Child, A F Brady, M Sarfarazi, K G Burnand, S Jeffery, P Mortimer, V A Murday. J Med Genet. 2002 Jul;39(7):478-83.
[13] Lymphoscintigraphic Abnormalities Associated with Milroy Disease and Lymphedema-Distichiasis Syndrome. Muberra Sarica, Kristiana Gordon, Malou van Zanten, Susan D Heenan, Peter S Mortimer, Andrew G Irwin, Vijaya Ramachandra, Pia Ostergaard, Sahar Mansour. Lymphat Res Biol. 2019 Dec;17(6):610-619.
[14] Primary non-syndromic lymphoedema (Meige disease) is not caused by mutations in FOXC2. Tayebeh Rezaie, Rose Ghoroghchian, Rachel Bell, Glen Brice, Ali Hasan, Kevin Burnand, Steve Vernon, Sahar Mansour, Peter Mortimer, Steve Jeffery, Anne Child, Mansoor Sarfarazi. European Journal of Human Genetics volume 16, pages300–304 (2008).
[15] Potential Utilization of Lymphoscintigraphy in Patients With Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome. Zhe Wen, Guansheng Tong, Yong Liu. Clin Nucl Med. 2021 Jan;46(1):25-30.