Learning objectives
The use of immune mediated treatment of cancer is improving dramatically the patient’s outcome and comfort, but it also carries new toxicity profiles. While standard antineoplastic therapy is associated with immunosuppression and infections, these new therapies induce overwhelming inflammation and autoimmunity. The vast majority of these adverse events can be classified as mild or moderate, but severe and life-threatening complications requiring ICU admission can also occur.
A considerable part of adverse effects related to immunotherapy can be diagnosed by imaging methods. This situation makes the...
Background
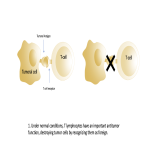
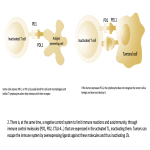
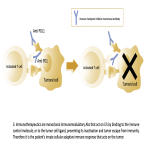
Immunotherapy potentiates the host's own adaptive immune system to stimulate an antitumor response. Tumor cells have created multiple mechanisms to evade destruction by the immune system such as disrupting effective antigen presentation, reducing efficacy of T-cell function and up-regulating pathways that promote tolerance and T-cell anergy. Immunotherapy attempts to disrupt the aforementioned mechanisms, and are grouped into different subtypes by their mechanisms of action. Checkpoint proteins are receptors expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes and help to down-regulate the immune system, when they are...
Findings and procedure details
Complications usually occur in the first 3 months of onset (up to 12 months) and resolve in about 2-3 months.There have been described a series of factors that favor the development of adverse events:
History of autoimmunity and chronic infections
Male sex
Renal failure (grade 3-4)
Combined therapies (PD1 + CTLA4)
Otherwise, the use of pretreatment corticosteroids and female sex are considered protective factors.
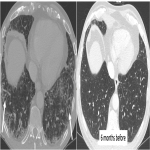
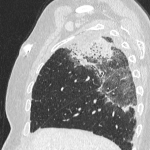
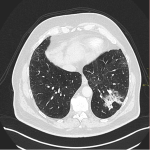
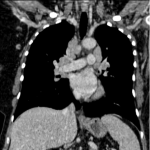
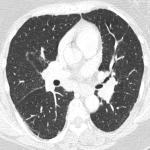
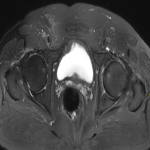
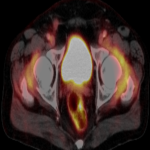
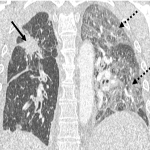
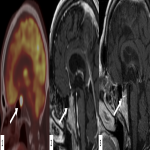
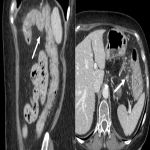
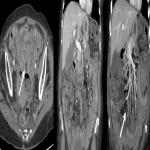
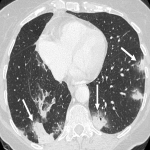
From the immune-related adverse effects described in the scientific literature, we found some cases of hypophysitis, synovitis, enteritis,different types of pneumonitis...
Conclusion
As the access to immunotherapy treatment is growing in the oncological setting, it is essential to be able to recognise imaging manifestations of these adverse effects in order to take part in the early diagnosis and optimal follow-up of these patients, pointing out the role of CT, PET-CT and MRI in this multidisciplinary approach.
Personal information and conflict of interest
S. LON COLVûE:
Nothing to disclose
M. Guerrero Martin:
Nothing to disclose
û. Rueda De Eusebio:
Nothing to disclose
S. Gû°mez PeûÝa:
Nothing to disclose
M. C. Polidura Arruga:
Nothing to disclose
N. Gomez Ruiz:
Nothing to disclose
P. Hernandez Mateo:
Nothing to disclose
I. Martin Lores:
Nothing to disclose
References
Tang YZ, Szabados B, Leung C, Sahdev A. Adverse effects and radiological manifestations of new immunotherapy agents. Br J Radiol 2019; 92: 20180164.
Nishino M, Hatabu H, Hodi FS. Imaging of Cancer Immunotherapy: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Radiology. 2019 Jan;290(1):9-22. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018181349. Epub 2018 Nov 20. PMID: 30457485; PMCID: PMC6312436.
Kwak JJ, Tirumani SH, Van den Abbeele AD, Koo PJ, Jacene HA. Cancer immunotherapy: imaging assessment of novel treatment response patterns and immune-related adverse events. Radiographics. 2015 Mar-Apr;35(2):424-37. doi: 10.1148/rg.352140121. PMID: 25763727.
Immune Checkpoint...