Purpose
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the leading causes of global cancer burden and a highly lethal disease in the metastatic state. Novel multimodal treatment strategies, including systemic therapy in combination with various local-ablative treatment options have shown promising results to improve patient outcomes. While radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation or transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) are frequently used in earlier stages of the disease, transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with Yttrium-90-loaded (Y-90) microspheres may be also considered as a treatment option with non-curative intent. As TARE is a costly...
Methods and materials
Study Design and Patient Selection
This institutional review board-proved study was performed as a retrospective single-center observational trial in a university liver center. Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective character of the study. All patients with TARE for hepatic mCRC and available pre-TARE imaging as well as follow-up data for response evaluation (n = 51), identified from the entire cohort with TARE (n = 288), in our center between 2009 and 2021 were included. All patients had experienced stable or progressive disease under...
Results
Patient characteristics
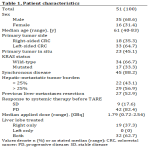
Fifty-one patients with hepatic mCRC and TARE were included [median age, 61 years (range: 40–83); n = 35 male, n = 16 female]. Prior to TARE, all patients received systemic therapy, with either stable (n = 9, 17.6%) or progressive disease (n = 42, 82.4). Detailed patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Response to TARE
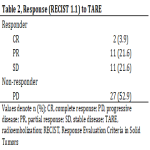
At the 3-month follow-up after TARE, n = 24 (47.1%) of the patients showed treatment response [complete response: n = 2 (3.9%), partial response: n = 11...
Conclusion
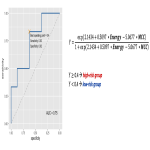
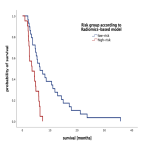
The radiomics-based model may predict the response and survival outcome in patients treated with TARE for colorectal liver metastases. Thus, this radiomics-based approach may provide an important decision tool for planning TARE and hereby optimize patient selection.
Personal information and conflict of interest
P. Schindler:
Nothing to disclose
M. Masthoff:
Nothing to disclose
M. Köhler:
Nothing to disclose
K. Rahbar:
Nothing to disclose
L. Stegger:
Nothing to disclose
W. Heindel:
Nothing to disclose
M. Wildgruber:
Nothing to disclose
W. Roll:
Nothing to disclose
References
Morsbach F, Pfammatter T, Reiner CS, et al. Computed tomographic perfusion imaging for the prediction of response and survival to transarterial radioembolization of liver metastases. Invest Radiol. Invest Radiol; 2013;48(11):787–794.
Sato KT, Omary RA, Takehana C, et al. The role of tumor vascularity in predicting survival after yttrium-90 radioembolization for liver metastases. J Vasc Interv Radiol. J Vasc Interv Radiol; 2009;20(12):1564–1569.
Garin E, Lenoir L, Rolland Y, et al. Dosimetry based on 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin SPECT/CT accurately predicts tumor response and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients...


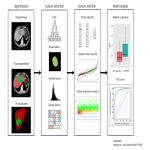
![Fig 2: Results of Feature Selection. Two independent features [Energy, Maximal Correlation Coefficient (MCC)] differentiated well between responders (green) and non-responders (red) to TARE at follow-up after 3 months according to RECIST 1.1 [responder (complete/partial response and disease control); non-responder (progressive disease)].](https://epos.myesr.org/posterimage/esr/ecr2023/164127/media/923241?maxheight=150&maxwidth=150)