Purpose
The purpose of this study is to present the optimization of CT examinations in 2022 in terms of radiation dose reduction in 8 diagnostic units where 9 CT scanners are operating. As part of the Affidea Dose Excellence Programme, we verify the CT examinations for quality assurance purposes. The main goal of the programme is to optimize CT examinations with doses that exceed the organizational Dose Refence Levels (DRLs).
Methods and materials
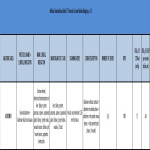
A common Radiation Dose Monitoring System (RDMS) in combination with a Business Intelligence (BI) tool were used to monitor CT dose data. 104 standardised CT protocols per anatomical area and clinical indication, with defined DRLs, allowed for practice standardization across all centres. Each protocol corresponded to an RPID code from the Radlex Radiology Lexicon with defined number of series and scan area description.
[Fig 1]
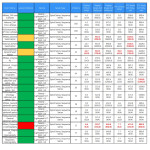
Dose data were collected centrally using the BI tool. Data was analysed and actions for improvement of protocol parameters and...
Results
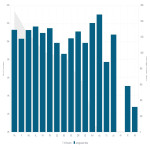
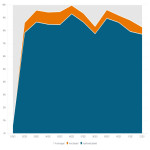
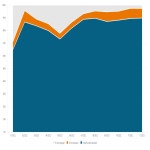
Annual data from 2021 and 2022 were compared using the business intelligence tool.
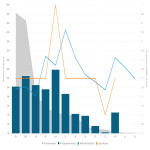
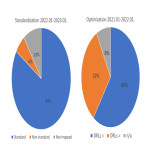
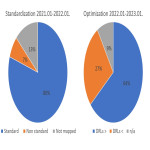
In 2021, a total of 44,274 CT scans were performed, of which 35,388 (80%) were performed with a standard number of series, 3,156 (7%) with a non-standard series, and 5,730 (13%) without an identifier (not mapped, missing RPID).
[Fig 6]
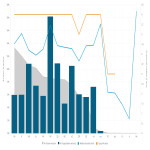
In terms of dose, 26,359 (59%) examinations were performed below the organizational DRLs, 14,360 (32%) exceeded DRLs, and 3,590 (8%) did not have a reference value.
[Fig 7]
After observing the data,...
Conclusion
In 2022, 84% of examinations were performed with the appropriate number of series as defined by the organizational CT standardized protocol list, increasing standardization by 4%. From the examinations performed with the appropriate number of series, 64% were performed with dose below DRL, increasing optimization by 5% compared to 2021.
The establishment of a robust Dose Management program aims to reduce Computed Tomography (CT) radiation dose levels by optimizing exposure and maintain diagnostic accuracy. Continuous monitoring, dose optimisation and personnel education improves patient safety in...
Personal information and conflict of interest
Z. Barbócz:
Nothing to disclose
C. Colmo:
Nothing to disclose
L. Kardos:
Nothing to disclose
G. Volford:
Nothing to disclose
C. Paraskevopoulou:
Nothing to disclose
A. Roncacci:
Nothing to disclose
References
1; K. Katsari, A. Papachristodoulou, C. Paraskevopoulou, R. Illing - Establishing a dose management strategy in Computed Tomography
DOI: 10.1594/esi2018/ESI-0022
2,; K. Katsari, R. Illing, A. Papachristodoulou, C. A. Ciortea, V. Herédia, S. Puggina, G. Volford, X. Boulanger, A. Kaczor - Implementation of a multi country CT Dose Management system
DOI: 10.1594/esi2016/ESI-0015
3; A. Papachristodoulou, A. Kaczor, G. Volford, K. Katsari, L. M. J. Best, D. Daravigkas, P. Rybicki, Z. Bikhazi, R. Illing;- Brain CT and radiation dose: analysis and comparison in terms of dose...