Background/introduction
The steadily increasing use of computed tomography (CT) in medical imaging in the last decades [1-4] has raised concerns about its potential associated cancer risk. Recent epidemiological studies have suggested an association between CT exposure and cancer risk in pediatric patients [5-7]. Following the ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) principle, the radiologic community, and CT vendors have made substantial efforts to decrease the radiation burden to patients by establishing imaging campaigns (e.g. image wisely [8] and image gently [9]) as well as by improving...
Description of activity and work performed
Materials and Methods
Phantom and Scan setup
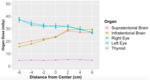
An anthropomorphic pediatric dosimetry phantom simulating a 5-year old child was imaged separately using vendor-specific protocols for head CT and thoracoabdominal CT. Multiple dosimeters were placed in different organs for both body regions (Fig.1). A scout image was acquired in lateral orientation in head CT and in anteroposterior orientation in thoracoabdominal CT.
The phantom was manually centered and imaged repeatedly at multiple vertical off-center positions (from -6 cm to + 6 cm compared to the 0-position). In head...
Conclusion and recommendations
Our study indicates that in pediatric CT, ATCM, organ radiation doses, and image noise were substantially affected by vertical patient positioning, with radiation dose differences compared to the 0-position of up to 34%. Our results extend the current body of literature for pediatric CT of the head and trunk by the following main findings: i) the impact of patient positioning depends on the body region and location of each individual organ within the body; ii). differences in organ dose are caused by both ATCM and...
Personal/organisational information
A. Euler; Zurich/CH - nothing to disclose H. Alkadhi; Zurich/CH - nothing to disclose N. Saltybaeva; Zurich/CH - nothing to disclose
References
1Mettler FA, Bhargavan M, Faulkner K et al (2009) Radiologic and nuclear medicine studies in the United States and worldwide: frequency, radiation dose, and comparison with other radiation sources--1950-2007. Radiology 253:520-531
2Bly R, Jahnen A, Järvinen H, Olerud H, Vassileva J, Vogiatzi S (2015) Collective effective dose in Europe from X-ray and nuclear medicine procedures. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 165:129-132
3Le Coultre R, Bize J, Champendal M et al (2016) EXPOSURE OF THE SWISS POPULATION BY RADIODIAGNOSTICS: 2013 REVIEW. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 169:221-224
4Pola A, Corbella...