Consultation types
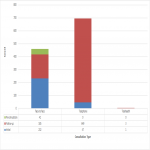
During the ten-week period, a total of 1159 consultations were performed across 973 patients.
Approximately sixty percent (700) of all consultations were performed by telephone/telehealth, with less than one percent of these by telehealth (4). The remaining forty percent of consultations were conducted face-to-face.
While initial consultations were more commonly performed face-to-face than via telephone/telehealth, the majority of follow-up consultations were conducted via telephone than face-to-face (Figure 1).
Subsequent face-to-face consultation
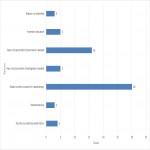
Sixty-six (9% of all telephone/telehealth) patients required a subsequent face-to-face consultation following their telephone/telehealth consultation within the study period.
The reasons for these face-to-consultations are outlined in Figure 2.
Patient subgroups
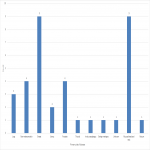
Of the 16 patients requiring a physical examination for a new clinical problem, the primary sites of disease were identified as: breast (4), mucosal head and neck (3), skin (3), endometrium (2), oral cavity (1), rectal (1), lung (1), and prostate (1).
Further, of the 5 patients requiring further investigation(s), the primary sites of disease, were: prostate (3), mucosal head and neck (1) and benign meningeal disease (1).
Routine examinations were performed on three breast cancer patients and one patient with a mucosal head and neck primary.
Figure 3 demonstrates the primary site of disease of those patients who attended for subsequent face-to-face consultations, excluding those who attended for written consent.