Purpose
In this study,
we evaluate the effect of different levels of iterative CT image reconstruction (IR) algorithms and convolution kernels on the quality of dynamic CT data for the quantitative estimation of myocardial blood flow (MBF).
In the daily clinical setting,
there is increasing awareness for the need to determine MBF quantitatively in ml/100g/min.
This highly important role of absolute MBF estimation deduces from increasing demands for therapeutic interventions in cardiovascular diseases.
MBF estimation is important not only in the evaluation of regional and global...
Methods and Materials
Phantom Study
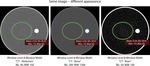
We simulated dynamic CT-based myocardial perfusion measurements using a phantom body containing sterilized water and a small teflon structure (see Fig.
2).
For all experiments 11 slices were acquired over 30 timesteps with a multi-row CT scanner (100kVp/100mAs,
reconstructed slice-thickness of 5mm,
exposure time 180ms,
12Bit).
Image Reconstruction
The images were reconstructed using
filtered back projection (FBP)
three different levels (strength) of an iterative reconstruction (IR) algorithm (iDose4,
level 2,
level 4 and level 6).
Image reconstruction was performed applying three different convolution...
Results
Phantom Study
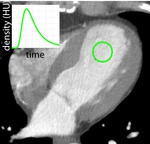
Large area water ROI (see Fig.
6)
Tab.
1: HU values of the image part corresponding to water (mean ± SD)
convolution
kernel
FBP
IR level 2
IR level 4
IR level 6
CA
3.5 ± 17.29
3.5 ± 14.77
3.5 ± 13.02
3.5 ± 10.72
CC
3.05 ± 34.54
3.05 ± 28.63
3.05 ± 24.54
3.05 ± 19.37
CD
8.8 ± 50.9
8.8 ± 42.23
8.8 ± 36.44
8.8 ± 29.27
Tab.
2: Minimal HU values of the image part corresponding to...
Conclusion
In this study,
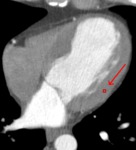
we quantitatively evaluated differences in absolute CT numbers resulting from various image reconstruction methods in simulated MBF measurements using a phantom body and MBF measurements of one patient.
The mean values of large ROIs and smaller ROIs in the images remain almost unchanged with different levels of iterative reconstruction.
The range of HU-values (MIN -- MAX) dicreases as well as the standard deviation.
Myocardial blood flow parameters also remained almost unchanged for all different reconstruction methods.
In conclusion,
we can confirm that...
References
Makarenko,
V.,
et al.
„Feasibility of rotational 256 row CT in measuring myocardial perfusion in anaesthetized dogs.“ European Congress of Radiology (ECR 2013),
EPOS. Wien,
2013.
Mehta,
D .,
R.
Thompson,
T.
Morton,
A.
Dhanantwari,
und E.
Shefer.
„ITERATIVE MODEL RECONSTRUCTION: SIMULTANEOUSLY LOWERED COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY RADIATION DOSE AND IMPROVED IMAGE QUALITY.“ MEDICAL PHYSICS INTERNATIONAL Journal,
2013: 147-154.
Whiting,
B.
R.,
Massoumzadeh,
P.,
Earl,
O.
A.,
O’Sullivan,
J.
A.,
Snyder,
D.
L.,
& Williamson,
J.
F.
(2006).
roperties of preprocessed sinogram data in x-ray computed tomography....