Purpose
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomoyopathy (ARVC) is characterized by fibrofatty infiltrationof the right ventricular (RV) myocardium,
which is an ideal structural substratefor reentrant ventriclar tachycardia (VT) (1).
Myocardial fat can be assessed with cardiac MDCTas areas of myocardial hypodensity,
but this feature is not part of current diagnostic criteria inARVC,
because of poor specificity and reproducibility (2).
However,
in patients with known ARVC,
the ability to non-invasively mapthepatient-specificstructural substrate could be of value to guide VT ablation.We studiedthe relationship between myocardial fat,
as assessed withan automatic...
Methods and Materials
Population
We studied 16 patients with definite ARVC according to Task Force Criteria,
referred for catheter ablation of VT.
MDTC acquisition and processing
Cardiac MDCT was performed using a contrast-enhanced cardiac-gated method on a 64-slicescanner,
using a biphasic injection protocol to optimize RV chamber enhancement.
On short axis reformats,
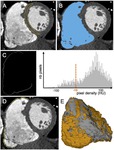
an automatic method was applied to map any area with pixel intensity <-10HU within a 2mm-thick RV free wall layer (Figure 1).
Three-dimensional cardiac objects comprising cardiac chambers,
epicardium,
fat segmentations and coronary vesselswere derived from...
Results
Clinical characteristics
Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
All patients had definite ARVC diagnosis according to Task Force criteria.
Of note,
14 (88%) of the patients were implanted with ICDs precluding the use of MRI.
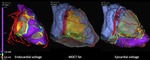
Electroanatomic mapping
All 16 patients were mapped endocardially,
and 13 were mapped epicardially.
The average number of mapping points was 626±335and 575±279 onRV endocardium and epicardium,
respectively.The bipolar low voltagearea was signicantly smaller onthe endocardium than onthe epicardium (46.6±28.6cm2versus 115.3±32.2 cm2,P<0.05).
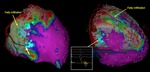
Local abnormal ventricular activities (LAVA) were found and...
Conclusion
Myocardial fat assessed with MDCT correlates to the electrophysiological substrate of VT in ARVC.
Ablation targets are clustered at the border of fat areas.
Further research is desirable to evaluate the impact of MDCT-integration during VT ablation on patient outcome in ARVC.
References
Marcus FI,
Fontaine GH,
Guiraudon G,
et al.
Right ventricular dysplasia: a report of 24 adult cases.
Circulation 1982;65:384-98.
Kimura F,
Matsuo Y,
Nakajima T,
et al.Myocardial fat at cardiac imaging: how can we differentiate pathologic from physiologic fatty infiltration? Radiographics 2010;30:1587-602