Purpose
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is characterized by increasing of pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary arterial pressure,
which leads to right ventricular failure [1].
The most common form of PH is a chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH).
It is the only potentially curable form of PH,
which is characterized by chronic obstruction of the pulmonary artery branches after a single or repeated thromboembolism.
Severe obstruction or complete occlusion of the pulmonary arteries contributes to the formation of typical perfusion defects,
finding of which is a crucial part...
Methods and Materials
Between November 2015 and May 2016 were examined 22 patients with a definite diagnosis of CTEPH (7 men,
15 women; range,
27-67 years).
All patients were examined on 320-detector row CT scanner (Aquilion ONE 640 VISION Edition,
Toshiba Medical Systems) using the standard protocol Lung substraction.
Scans have been acquired in the supine position,
in craniocaudal direction,
during breath-hold at the maximum depth of the breath in non-contrast and arterial phases with the same parameters in the beginning and in the end of the scan....
Results
20 patients had thrombotic masses in both pulmonary arteries.
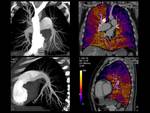
17 patients in this group were evaluated areas of severe perfusion decrease in both sides (fig.
1 and 2 a,
b).
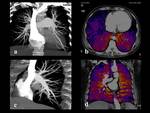
Three patients (15%) had a moderate perfusion decrease. There were no evidences of thrombosis in two patients; however,
the depletion of vascular pattern and segmental arteries with intraluminal bands and webs was detected (fig.
2c,
d). In the one case noted a moderate decrease in perfusion in the other - marked reduction in perfusion.
The...
Conclusion
Subtraction CT pulmonary angiography is the method,
which allows to quantify presence and severity of perfusion defects in patients with distal pulmonary artery thrombosis.
Also severity of perfusion defects is correspond to degree of vascular obstruction.
References
1.McLaughlin VV,Archer SL,Badesch DB,
et al.,ACCF/AHA 2009Expert Consensus Document on Pulmonary Hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol,2009.53(17): p.
1573-619.
2.Chae EJ,Seo JB,Jang YM,Krauss B,Lee CW,Lee HJ,Song KS.,Dual-energy CT for assessment of the severity of acute pulmonary embolism: pulmonary perfusion defect score compared with CT angiographic obstruction score and right ventricular/left ventricular diameter ratio.AJR Am J Roentgenol,2010.
194(3): p.
604-10.
3.
Yu T,
Yuan M,
Zhang Q,
Shi H,
Wang D,
Evaluation of computed tomography obstruction index in guiding therapeutic decisions and monitoring percutanous catheter fragmentation in massive...