Learning objectives
1.
To learn the relevant pathophysiology of Hydrocephalus.
2.
To learn the physics of cine mode (Phase contrast) MRI brain sequences and detail the acquisition protocols,
including tips and tricks.
3.To define an approach to interpretation of the Cine Mode (Phase-Contrast) images,
as an adjunct to conventional sequences in pre- and post –operative evaluation of Hydrocephalus
Background
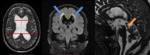
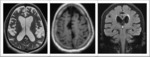
Hydrocephalus is usually defined as ventriculomegaly with sulcal effacement and can be classified as communicating,non- communicating or Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.
Communicating Hydrocephalus is implied if the level of the obstruction is distal to the 4th ventricle while non communicating hydrocephalus is implied if the level of obstruction is cranial to the 4th ventricular outflow.
Normal Pressure hydrocephalus is a special sub-class of hydrocephalus with disproportionate ventricular dilatation relative to sulcal prominence.
All causes of hydrocephalus are typically treated by shunt procedures,
with external shunt procedures...
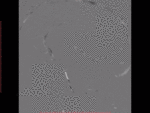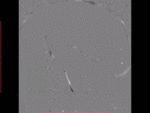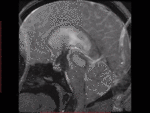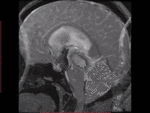
Findings and procedure details
Physics & Technique
CSF Flow is pulsatile & is synchronized to cardiac pulsations,
with a phase difference between cardiac pulsations and CSF pulsations,
resulting in caudad CSF flow during cardiac systole and cephalad CSF flow during cardiac diastole.
Typical CSF flow velocities are in the range of 5 to 8 cm/s.
In hyperdynamic circulations,
velocities can go up to 25 cm/s.
Time-resolved 2D phase contrast imaging with velocity encoding uses Phase encoding pulses in opposing directions,
sensitized to a velocity (called VENC- Velocity Encoding).
In...
Conclusion
Proper evaluation ofhydrocephalus on MRI needs a basic understanding of physiology of CSF flow dynamics as well the physics behind the MRI protocols.
Correct imaging plan including the protocol parameters and planes of imaging isas important as the knowledge of imaging presentations to avoid misinterpretation and misdiagnosis.
References
Black,
P.
M.,
Ojemann,
R.
G.
& Tzouras,
A.
CSF shunts for dementia,
incontinence,
and gait disturbance.
Clin Neurosurg 32,
632–651 (1985).
Armonda,
R.
A.,
Citrin,
C.
M.,
Foley,
K.
T.
& Ellenbogen,
R.
G.
Quantitative cine-mode magnetic resonance imaging of Chiari I malformations: an analysis of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
Neurosurgery 35,
214–223; discussion 223-224 (1994).
Ellenbogen,
R.
G.,
Armonda,
R.
A.,
Shaw,
D.
W.
& Winn,
H.
R.
Toward a rational treatment of Chiari I malformation and syringomyelia.
Neurosurg Focus 8,
E6 (2000).
Bargalló,...