Learning objectives
Review the basic anatomy of the scrotum.
Describe a stepwise approach for sonographic evaluation of the scrotum.
Discuss and illustrate the key sonographic imaging findings of scrotal emergencies.
Background
The acute scrotum is defined as sudden intense scrotal pain with associated swelling and tenderness, in which systemic symptoms may be present including nausea, vomiting, and fever. The diagnostic etiologies leading to acute scrotum are vast, with considerations based on the patient’s age. Etiologies include testicular torsion, infectious processes, and scrotal trauma. Ultrasound (US) is the gold standard imaging modality for the evaluation of acute scrotal pain. The goal of early ultrasound evaluation is to rule out testicular injury, especially in young patients in which...
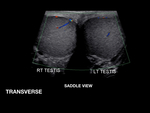
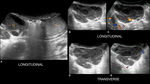
Findings and procedure details
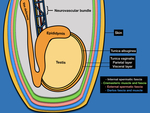
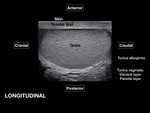
Anatomy Review
The scrotal sac is divided at midline by a septum, each half containing a testis and associated structures[2]. The scrotal sac has several layers that cannot be distinguished using USFig. 1.The tunica vaginalis is composed of two layers: the parietal layer lining the scrotal wall and the visceral layer lining the testicle and epididymis [1,2,7]. The space between the layers of the tunica vaginalis creates a potential space for fluid accumulation. The visceral layer of the tunica vaginalis adheres to the tunica albuginea,...
Conclusion
Ultrasound is a highly valuable imaging modality for the evaluation of scrotal emergencies. Differential diagnosis may be vast, with diagnostic considerations based on patient’s age. Scrotal traumatic injury, testicular torsion and infectious processes are important diagnosis every radiologist should recognize.
Personal information and conflict of interest
L. R. Rodriguez-Ortiz; San Juan, PR/US - nothing to disclose W. Rodriguez-Mojica; San Juan, PR/US - nothing to disclose X. E. Lopez Garib; San Juan, PUERTO RICO/US - nothing to disclose A. Saldana; San Juan, PR/US - nothing to disclose O. Concepcion; Dorado, PR/US - nothing to disclose
References
Dogra, V. S., Gottlieb, R. H., Oka, M., & Rubens, D. J. (2003). Sonography of the Scrotum1. Radiology, (227), 28–33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2271001744
Avery, L. L., & Scheinfeld, M. H. (2013). Imaging of Penile and Scrotal Emergencies. RadioGraphics, 33(3), 721–740. doi: 10.1148/rg.333125158
Bandarkar, A. N., & Blask, A. R. (2018). Testicular torsion with preserved flow: key sonographic features and value-added approach to diagnosis. Pediatric Radiology, 48(5), 735–744. doi: 10.1007/s00247-018-4093-0
Bhatt, S., & Dogra, V. S. (2008). Role of US in Testicular and Scrotal Trauma. RadioGraphics, 28(6),...