The Elastographic techniques are rapidly becoming the method of choice for the assessment of liver fibrosis, replacing liver biopsy for more than ten years for diagnosis, follow-up and treatment monitoring.
Stiffness and Elasticity
Tissues have proper elasticity that can be studied to provide to the clinicians some information about the liver disease.
Elasticity is the property of a material or a tissue to deform under a given stress and then to restore to its original shape after distortion.
Tissue Elasticity and Shear Waves
The 2D Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE) is an acoustic radiation force impulse technique (ARFI) used for the liver stiffness assessment.
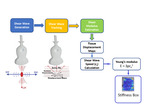
SWE technology is characterized by the generation of shear waves by the push pulse of an ultrasound focused beam, which creates some localized perturbations in a small region around the focus shock point.
In soft tissue, two modes of waves propagation occur:
- Longitudinal waves (LW)), in which the waves propagate in the same direction of particles oscillation
- Transverse waves or shear waves (SW), in which the waves propagate in the transverse direction respect to the particles oscillation. The transverse waves propagation speed is called Shear Wave Speed or Shear Speed (Cs). Shear wave Speed is usually displayed on the ultrasound system in m/s and may be converted using the Young’s modulus (E) in kPa:
ρ is the tissue density, assuming that the tissue is purely elastic, incompressible, that its elastic response is linear and that the tissue density is always 1000kg/m3
The 2D-SWE alternates multiple perturbations and reading phases, enabling an image of the shear waves speed for a small tissue sample, in which the clinicians can perform a measurement to get a quantitative assessment of the liver stiffness.
The Figure 1 resumes the basic principle behind SWE.
Shear Waves Elastography and Liver Stiffness Assessment
According to the Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography of the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB), 2D-SWE can be used to assess the severity of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis.
The aim of this technique is the measurement of the liver stiffness, which is related, to fibrosis stages, to evaluate the presence of no/initial (F0-1), mild (F2), advanced fibrosis (F3-4).
Due to several advantages, ultrasound 2D-SWE technique is becoming one of the methods of choice for the assessment of liver fibrosis; it is:
- a non-invasive method
- an ultrasound guided-imaging technique
- a complementary to a B-mode liver evaluation
- less expensive than MRI Elastography
- more available than MRI Elastography
- a repeatable technique
Nevertheless, in order to get reliable assessments of the stiffness, the clinicians must follow some precise recommendations during the procedure, in order to obtain a valid and reliable evaluation for the optimal manage of the patient.