Keywords:
Emergency, Head and neck, CT, Computer Applications-Detection, diagnosis, Diagnostic procedure, Inflammation, Neoplasia, Trauma
Authors:
R. Skumbiņš, S. Dzelzite, P. Prieditis, M. Radzina; Riga/LV
DOI:
10.26044/ecr2021/C-12606
Methods and materials
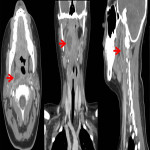
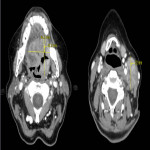
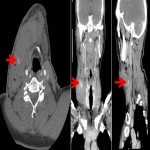
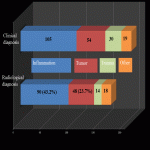
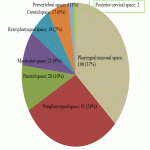
1. Retrospectively patients were analysed with emergency CT imaging in „Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital” in years of 2018 and 2019 for neck pathologies, their locations, characteristic radiological signs, changes in neck lymph nodes (location, changes which describe specific, non-specific lymph nodes), other radiological methods and also laboratory data correlation.
2. Additionally was evaluated patient clinical symptoms, documentation, otolaryngologist findings, used treatment (medical, surgical), histological and cytological findings, if they were performed.
3. Retrospectively was analysed CT role in case of emergency imaging and the correlation with clinical data and laboratory changes.
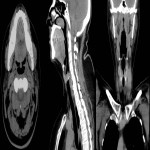
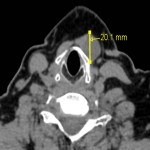
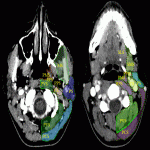
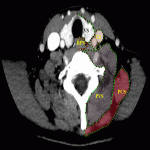
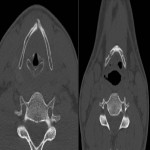
4. Examination protocol: CT topogram without contrast in axial plane from nose till aortic bifurcation (Fig.1.). One post contrast examination was performed with an aim to reduce the radiation dose for the patient. To exclude vascular injury or to differentiate inflammatory and oncology changes - arterial, venous and delayed post contrast examination was performed.