Purpose
A detailed assessment of CT examinations of the neck soft tissues gives possibility for an accurate differential diagnosis based on the involvement of interfascial spaces and other radiological signs, radiological-clinical combined signs of neck pathological changes if tailored CT examination protocol in emergency department is applied.
Methods and materials
1. Retrospectively patients were analysed with emergency CT imaging in „Pauls Stradins Clinical University Hospital” in years of 2018 and 2019 for neck pathologies, their locations, characteristic radiological signs, changes in neck lymph nodes (location, changes which describe specific, non-specific lymph nodes), other radiological methods and also laboratory data correlation.
2. Additionally was evaluated patient clinical symptoms, documentation, otolaryngologist findings, used treatment (medical, surgical), histological and cytological findings, if they were performed.
3. Retrospectively was analysed CT role in case of emergency imaging and the...
Results
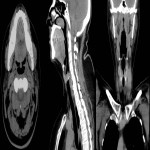
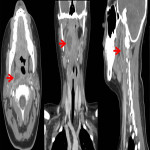
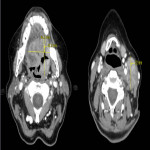
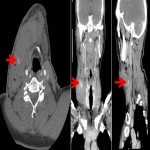
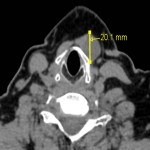
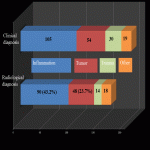
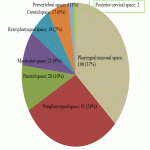
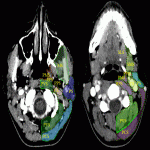
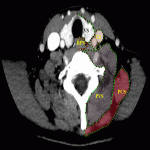
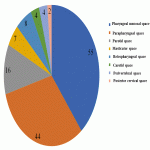
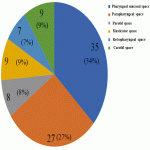
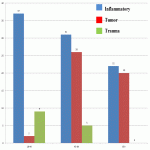
Neck soft tissue pathology was found in 175/208 cases: 90 cases inflammatory changes (Fig.2.), 48 cases oncology (Fig.3.), 14 cases trauma (Fig.4.) and 18 cases other pathology, for example congenital pathology (Fig.5.,6.). Most cases showed involvement above os hyoideum - pharyngeal space (n=100), parapharyngeal space (n=81), parotid (n=28), masticator (n=21), less often retropharyngeal (n=18), carotid, (n=17), perivertebral (n=4) and posterior cervical space (n=2) (Fig.7.,8.,9) [Fig 2] [Fig 3] [Fig 4] [Fig 5] [Fig 6] [Fig 7] [Fig 8] [Fig 9]
Most commonly inflammation and abscess...
Conclusion
1.CT examination of the soft cervical tissue at the emergency early stage is available and fast to determine the type of pathology, prevalence, complications and subsequent planning of treatment tactics, especially in 3 major groups of pathologies – tumors, inflammation and trauma.
2. In the evaluation of soft cervical tissues in patients with clinical suspicion of oncology - contrast-enhanced 3-series CT protocol is advised to assess the extension and vascularization characteristics, in inflammatory and other benign cases non-enhanced CT and 100th enhanced second examination is...
Personal information and conflict of interest
R. Skumbiņš:
Nothing to disclose
S. Dzelzite:
Nothing to disclose
P. Prieditis:
Nothing to disclose
M. Radzina:
Nothing to disclose
References
1.Rashmeet Kaur et al.:Role of Computed Tomography in localisation and characterisation of suprahyoid neck masses, 2017;263-270.
2. Kawabata M et al: Clinical classification of peritonsillar abscess based on CT and indications for immediate abscess tonsillectomy. 2016; 182–86
3. Hoang, J et al: Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Nodes in Head and Neck Cancer With CT and MRI; 2013;17-25