Type:
Educational Exhibit
Keywords:
Cardiovascular system, Ultrasound-Colour Doppler, Contrast agent-other, Arteriosclerosis
Authors:
A. Lioznovs, M. Radzina, L. Saule, I. Briede
DOI:
10.26044/ecr2022/C-19894
Learning objectives
Incidence of ischemic stroke every year increases worldwide, according to the World Health Organization ischemic stroke in 2017 were 1.12 million incident strokes in the European Union. It is projected that in Europe stroke events in future will rise from 1.1 million in 2000 to 1.5 million per year by 2025, making it the second commonest cause of death. Therefore, it is necessary to understand stroke risk factors, treatment options, mortality reduction options and disease outcomes. Diseases affecting the carotid arteries can lead to acute and chronic blood supply disorders and complications that can be life-threatening and restrict quality of life for patients. Carotid artery atherosclerotic pathology causes narrowing of the vascular lumen, changes in haemodynamic, therefore, increases the risk of transient ischemic attacks and cerebral infarction.
Stroke is a heterogeneous, multifactorial disease whose risk factors can be divided into two groups:
- independent risk factors: age, gender, race;
- risk factors that can be managed: arterial hypertension, diabetes, smoking, coronary heart disease, heart rhythm disorders, hyperlipoproteinemia, and others.
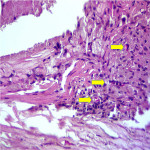
Mentioned risk factors lead to damage of the carotid artery wall and atherosclerotic plaque formation.
Atherosclerotic plaques can be of various types and stability:
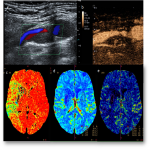
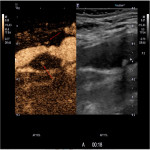
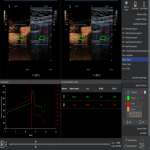
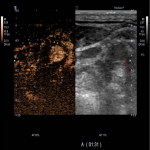
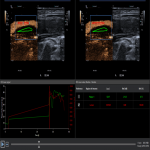
- Unstable plaques - plaques with ulcerations, pronounced hypoechogenic plaques, irregularity of the plaque surface, reduced density of the plaque and neovascularization.
- Partially stable plaques - heterogeneous atherosclerotic plaques without the signs of instability mentioned above.
- Stable plaques- hyperechogenic, calcified plaques.
One of the most significant reasons for high stroke incidence in presence of vessel stenosis, but undetected high-risk plaque. Unstable plaque abruption and embolization to intracerebral artery is one of main ischemic stroke cause. Therefore, accurate and timely detection of carotid atherosclerotic plaque and evaluation of its structural instability can help ensure timely patient optimal treatment algorithms. Subsequently new knowledge such as accurate and timely detection (diagnosis) of carotid atherosclerotic plaque and evaluation of its structural instability can help ensure timely patient optimal treatment algorithms, that can affect indirectly reduction of stroke risk and incidence and provide effective cost reduction, which are essential for surgical and conservative treatment decisions in individualized patient management.1