Type:
Educational Exhibit
Keywords:
Cardiovascular system, Ultrasound-Colour Doppler, Contrast agent-other, Arteriosclerosis
Authors:
A. Lioznovs, M. Radzina, L. Saule, I. Briede
DOI:
10.26044/ecr2022/C-19894
Background
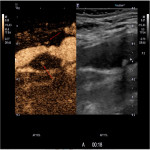
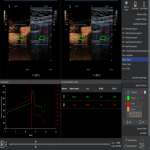
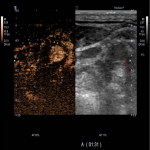
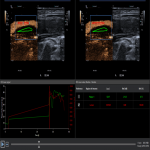
Nowadays in clinical practice there is a necessity for early detection of new biomarkers that will significantly reduce the risk of ischemic stroke, improve prognosis, and effectively customize treatment options for each patient. Duplex Doppler ultrasonography with high frequency probe allows adequate visualization and evaluation of carotidarteries in both duplex Doppler mode and B mode (greyscale ultrasound). Visibility of vascular flow may be difficult due to atherosclerotic vessel damage. In such cases, a microbubble contrast agent can be used as signal booster to improve the detection of blood flow.2
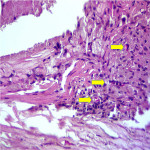
Vasa vasorum has a major role in the development of atherosclerotic plaque and it is one of the indicators of atherosclerotic plaque growth and progression, connected to the supply of oxygen and other nutrients, leading to the production and release of cytokines, adhesion molecules, growth factors in the atherosclerotic plaque, that stimulates plaque growth and destabilisation. Vasa vasorum infiltration increases intramural microvascular damage with following internal haemorrhage, which is one of the causes of plaque instability.3,4
The ultrasound contrast agent usually consists of encapsulated microbubbles, when administered intravenously - improves the resolution between blood vessels and tissues within 3 to 5 minutes period. Gas-filled microbubbles, due to the large difference in acoustic impedance between gas and liquid, help to identify and evaluate blood vessels with very low flow rates. Low ultrasonic wave power causes linear fluctuation of microbubbles by transforming them into small "transmitters". Thus, microbubbles improve the accuracy of stenosis diagnostics, help locate blood vessels with a very slow flow (including neovascularization and micro vascularization in blood vessels, other organs). In contrast, a short-term "flash" causes a microbubble cover rupture that creates an enhanced ultrasonic signal that can be perceived with high sensitivity. One of the main advantages of contrast ultrasound is the detection of new vessels (neovascularization) in the atherosclerotic plaque, thus facilitates the plaque's instability detection, awareness of ischemic cerebral stroke risk and can become a follow-up imaging tool before and after appropriate medication therapy.
The results of the studies show that the CEUS has greater accuracy in the determination of atherosclerotic haemodynamically significant stenosis than in conventional duplex Doppler ultrasonography. Contrast enhanced ultrasonography can not only accurately reflect the stenosis of carotid artery lumen, but also produce a Doppler signal in a longer period than in duplex dopplerography. The results of CEUS carotid artery stenosis measurement are comparable to the results of computed tomography angiography (CTA) (r = 0.988, p <0.01) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRI)(r = 0.979, p <0.01), but, unlike CTA, ultrasound contrast output from the body is not associated with kidney function, it is not nephrotoxic, patients are less likely to have allergic reactions and it is possible to take multiple doses of the contrast agent in a short period of time, and during the examination the patient does not have any ionizing radiation exposure that is very important.5,8