Purpose
To explore the use of popular natural language processing models to reframe radiology reports into a more simplified, concise format and improve ‘readability’ for patients.
In simpler terms, our goal was to see if ChatGPT could make complicated medical reports easier to read.
Methods and materials
Background:Radiologists play a critical role in communicating important clinical information identified through medical imaging, and the radiology report is the cornerstone of this process. While primarily directed to the referring clinician, information in the report may be sought by stakeholders beyond the immediate referrer, and increasingly, patients themselves may access and interpret their reports.1
The medical lexicography used in a typical report is often optimised for the referring doctor, but can pose a barrier to a patient less familiar with such jargon, limiting an opportunity...
Results
Results:Thirty studies from the emergency department were selected, ensuring a mix of ‘positive’ and ‘normal studies’. This consisted of 10 CT abdomen, 10 CT chest/CTPA and 10 trauma pan-scan studies. These studies had a variety of authors ranging from consultant radiologists (6 reports) to senior (14) and junior registrars (10).
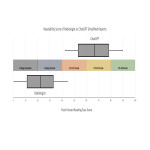
The average FKRE score of the original conclusions was 20.3 (standard deviation 17.1) corresponding to a reading level for university educated graduates. After simplification by ChatGPT, the average score increased to 65.2 (standard deviation 15.7)...
Conclusion
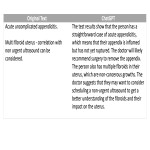
Natural language processing models can generate simplified summaries of radiology reports, providing relevant information in a clear and concise format optimised for patient interpretation. However, there is still the potential for erroneous information to be added, therefore radiologist oversight remains paramount.
References
References:
Goldberg-Stein S, Chernyak V. Adding Value in Radiology Reporting. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019;16(9, Part B):1292-1298. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2019.05.042
King A, Hoppe RB. “Best Practice” for Patient-Centered Communication: A Narrative Review. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(3):385-393. doi:10.4300/JGME-D-13-00072.1
Bowen S. The Impact of Language Barriers on Patient Safety and Quality of Care. Final Rep.
Riedl D, Schüßler G. The Influence of Doctor-Patient Communication on Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Z Für Psychosom Med Psychother. 2017;63(2):131-150. doi:10.13109/zptm.2017.63.2.131
6617.pdf. Accessed August 20, 2023. http://lib.ncfh.org/pdfs/6617.pdf
Abu-Heija AA, Shatta M, Ajam...