Learning objectives
Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) is a high-spatial-resolution 3D gradient-echo MR imaging technique to enhance contrast by accentuating the paramagnetic properties of blood product.
The aim of this pictorial review is to outline the basic physics of Susceptibility weighted imaging and to describe different applications of Susceptibility-weighted imaging in neuroimaging.
Background
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI),
originally called BOLD venographic imaging is an imaging technique developed by Haacke et al in 2004.
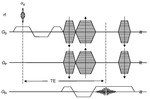
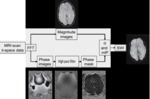
SWI is a fully velocity compensated high-resolution 3D gradient-echo sequence that uses magnitude and filtered-phase information to create a different form of contrast.
This technique exploits the susceptibility differences in tissues such that signal from substances with different susceptibilities than their neighbouring tissues (such as venous blood or haemorrhage) will become out of phase.
This special data acquisition and image processing produces an enhanced contrast...
Findings and procedure details
Basic Physics of Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
Compounds which have paramagnetic,
diamagnetic and ferromagnetic properties all interact with the local magnetic field distorting it and thus altering the phase of local tissue which in turn results in loss of signal.
Paramagnetic compounds include deoxyhaemoglobin,
ferritin and hemosiderin and diamagnetic compounds include bone minerals and dystrophic calcifications.
This new method exploits the susceptibility differences between tissues.
SWI uses a fully velocity compensated,
three dimensional,
rf spoiled,
high-resolution,
3Dgradient echo scan.
Signal from substances with different susceptibilities than...
Conclusion
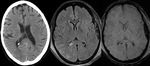
SWI allows improved visualisation of hemorrhage,
iron deposition in gray matter and venous structures in brain improving the lesion detection with better diagnosis of disease and efffect on patient management and prognosis.
References
Haacke EM,
Mittal S,
Wu Z,
Neelavalli J,
Cheng YC.
Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications,
part 1.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Jan;30(1):19-30.
Mittal S,
Wu Z,
Neelavalli J,
Haacke EM.
Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications,
part 2.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Feb;30(2):232-52.
Basic study of susceptibility-weighted imaging at 1.5T.
Matsushita T,
Anami D,
Arioka T,
Inoue S,
Kariya Y,
Fujimoto M,
Ida K,
Sasai N,
Kaji M,
Kanazawa S,
Joja I.
Acta Med Okayama.
2008;62:159-68.
Tong KA,
Ashwal S,...