This poster is published under an
open license. Please read the
disclaimer for further details.
Keywords:
Dosimetric comparison, Diagnostic procedure, CT, Radioprotection / Radiation dose, Oncology
Authors:
E. Lekgabe, N. Tran, W. Cheung, B. McDonald, H. Kavnoudias, L. Hudson, X. Chen; Melbourne/AU
DOI:
10.1594/ecr2015/C-1895
Methods and materials
Seventy oncology patients with previous conventional contrast enhanced (CE) CT CAP referred for restaging or surveillance CE CT CAP were imaged using the proposed protocol of two contrast injections and single-pass acquisition.
The patients were all adult outpatients referred for restaging or surveillance scans.
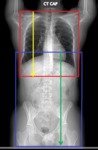
The conventional protocol at our institution is acquired in two segments (figure 1):
-
Chest: from above the lung apices to below the diaphragm.
-
Abdomen/pelvis: from above the diaphragm to ischial tuberosities.
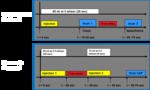
A single bolus of 80 ml of iodinated contrast (350ml/g) is used and administered at rate of 3ml/sec (figure 2).
On the other hand,
the research protocol was performed by dividing the volume of contrast into two boluses of 65 ml and 15 ml and administered separately.
The 65 ml bolus was administered from 0 seconds (at a rate of 2.5 ml /sec) and the 15 ml bolus administered from 39 sec (rate: 2.5 ml/sec) (figure 2).
The CT CAP scan was then acquired in a single-pass acquisition at around 50 to 70 seconds.
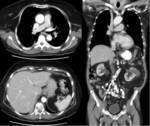
A sample of the images obtained from a research protocol scan is shown in figure 3.
Auto bolus tracking software and automatic exposure control (AEC) were used in both scan protocols.
All the scans,
including the conventional protocol scans,
were performed with the same scanner,
GE LightSpeed VCT 64 slice (GE Healthcare,
Milwaukee,
WI,
USA).
The parameters measured include:
-
The dose-length-product (DLP) for the research and conventional protocol scans of each patient was recorded.
-
The image quality was retrospectively and individually evaluated by two experienced radiologists.
The radiologists received a randomised list of the 140 scans,
meaning each patient’s two scans were not directly compared side by side.
Each scan was given an image quality score using a 4-point scale,
1 represeting poor,
2 - moderate,
3 - good and 4 - excellent image quality.
Inter-observer agreement (kappa) was calculated.
The image quality scores for the two different scans were compared.
-
Radiographers performing the research protocol scans graded the ease of performing the scans,
when compared to the conventional protocol,
on a 5-point scale,
1 representing much easier,
3 not different and 5 much more difficult than the conventional protocol scan.
-
Attenuation values (Hounsfield units) of the aortic arch,
pulmonary trunk,
liver and spleen.
The study was approved by the human research and ethics committee at our institution.