Learning objectives
-To review the CT and MRI appearance of the cirrhotic liver.
-To describe thepathologic conditions that can mimic cirrhosis.
Background
Cirrhosis is the end result of every chronic diffuse liver disease from various etiologies.
The most common causes are hepatitis B and C viral infection,
alcohol abuse,
and non alcoholic fatty liver disease.Cirrhosis is pathologically characterized by distortion of hepatic architecture due to marked bridging hepatic fibrosis and regenerative nodule formation.
In this educational exhibit,
we describe the morphologic signs of cirrhosis,
and provide useful tips to recognize a cirrhotic liver and to differentiate the cirrhotic liver from other conditions that can mimic cirrhosis.
Findings and procedure details
A non invasive diagnosis of cirrhosis can be done at CT and MRI by identifying hepatic and extrahepatic signs of cirrhosis.
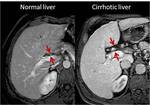
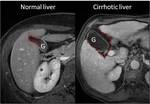
HEPATIC SIGNS
At earlier stages of cirrhosis,
the liver can appear normal or show only subtle heterogeneity.
With disease progression,
characteristic regional changes in hepatic morphology are seen,
such as hypertrophy of the caudate and left lobes and atrophy of the segment IV.
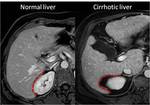
Enlarged hilar periportal space
An enlarged hilar periportal space (defined as a distance between the right portal vein and the posterior...
Conclusion
CT and MRI signs of cirrhosis can help radiologists make a non invasive diagnosis of cirrhosis and differentiate cirrhosis from its mimics.
References
Friedman SL.
Liver fibrosis -- from bench to bedside.
J Hepatol.
2003;38 Suppl 1:S38-53.
Tan KC.
Enlargement of the hilar periportal space.
Radiology.
2008 Aug;248(2):699-700.
Tan KC.
The right posterior hepatic notch sign.
Radiology.
2008 Jul;248(1):317-8.
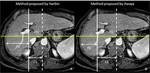
Harbin WP,
Robert NJ,
Ferrucci JT Jr.
Diagnosis of cirrhosis based on regional changes in hepatic morphology: a radiological and pathological analysis.
Radiology.
1980 May;135(2):273-83.
Awaya H,
Mitchell DG,
Kamishima T,
et al.
Cirrhosis: modified caudate-right lobe ratio.
Radiology.
2002 Sep;224(3):769-74.
Ito K,
Mitchell DG,
Kim MJ,
et al....