Keywords:
Breast, Computer applications, Mammography, Neural networks, Computer Applications-Detection, diagnosis, Efficacy studies
Authors:
E. F. Conant1, S. Periaswamy2, S. Fotin2, J. Go2, J. Pike2, J. boatsman3, J. Hoffmeister2; 1Philadelphia, PA/US, 2Nashua, NH/US, 3San Antonio, TX/US
DOI:
10.26044/ecr2019/C-1648
Results
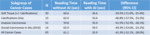
The sensitivity subgroup analysis in Table 1 shows that average radiologist sensitivity improved 6.8% with AI for soft tissue and 6.2% for invasive carcinomas,
with larger improvements of 12.0% for calcifications-only and 14.6% for DCIS.
Of note,
all 95% CIs were above zero,
indicating strength of these improvements.
For all cancer cases,
average radiologist sensitivity improved 8.0% (95% CI: 2.6%,
13.5%) from 77.0% without AI to 85.0% with AI.
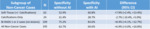
Subgroup analysis of reading time in cancer cases (Table 2) shows that average radiologist reading time was reduced 39.5% with AI for soft tissue and 41.5% for invasive carcinomas,
with a similar 40.3% reduction for DCIS and a possibly larger 46.8% reduction with calcifications-only.
All reductions in reading time had 95% CIs well below zero,
indicating strong reductions.
For all cancer cases,
average radiologist reading time was reduced 41.3% (95% CI: 28.0%,
52.1%) from 61.1 seconds without AI to 35.9 seconds with AI.
The specificity subgroup analysis in Table 3 shows that average radiologist specificity improved 7.9% with AI for soft tissue and 8.4% for BI-RADS 1 or 2,
but did not for calcifications-only at -2.7%.
The strength of the specificity improvements for soft tissue and BI-RADS 1 or 2 were indicated by 95% CIs that were above zero,
but the 95% CIs included zero for calcifications-only,
indicating little change in specificity.
For all non-cancer cases,
average radiologist specificity improved 6.9% (95% CI: 3.0%,
10.8%) from 62.7% without AI to 69.6% with AI.
Subgroup analysis of reading time in non-cancer cases (Table 4) shows that average radiologist reading time was reduced 54.4% with AI for soft tissue with a similar 59.1% reduction for BI-RADS 1 or 2 and a possibly smaller 43.6% reduction with calcifications-only.
All reductions in reading time had 95% CIs well below zero,
indicating strong reductions.
For all non-cancer cases,
average radiologist reading time was reduced 55.9% (95% CI: 45.5%,
64.4%) from 65.1 seconds without AI to 28.7 seconds with AI.