Purpose
Nosocomial infectionsare a public health problem and responsible for the death of milion. [1,2]
This infections compromise patients as a result of health care procedures and may also affect Professionals. [2]
Considering that thehands of Professionals are the most common vehicle of this transmissionand paying attention to theincreasing use of mobile phones in hospitals, it is important to adopt preventive measures. [3]
Among these measures,hands hygienizationis the most important to interrupt the infections epidemiological chain, but if we take this into account with disinfection of...
Methods and materials
Population: The data collection was realized in a Public Hospitalbetween Juneand November 2018to28 Radiographers.
Radiographers Knowledge Evaluation
A self-applied questionnaire and informed consent about microorganisms transmission, hands hygienization and the use and disinfection of mobile phones during their clinical practice was applied.
Microorganisms Identification
The Radiographers mobile phones andworkstations of Conventional Radiology andCT were swabbed with Stuart transports medium using a standardized and aseptic technique to check the contamination.
The swabbed of mobile phones were obtained from both sides and performed before and after their...
Results
Questionnaire Data
23 participants (82.1%) considered that the hands hygienization have a high impact on nosocomial infections prevention;
20 (71.4%) Radiographersknow that the hands arethe most common vehicle of pathogenic microorganisms transmission;
All the participants use their mobile phones in hospital;
23 (82.1%) doesn’tdisinfect their mobile phone.
Knowledge
We selectseven questions and evaluate the number of correct answers.
16 Radiographers(57.1%) had a correct percentage of responses between 25 and 50%.
Only 1 (3.6%) between 75 and 100%(Fig. 4).
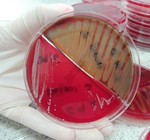
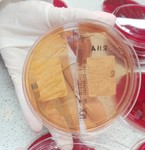
Contamination and Microorganisms
The contamination rate in...
Conclusion
It is possible to conclude that:
Radiographers have low knowledge about hands hygienization and microorganisms transmission.
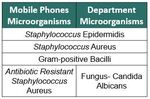
In majority, bacterial growth confirmed that mobile phones microorganisms are the same genus as those identified in the Radiology Department.
The number of colonies after clinical practice was superior in only three Radiographers.
This research confirmed the great diversity ofmicroorganismsin mobile phones such as Oxacillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus.
In conclusion, mobile phones use doesn’t have risks of pathogenic microorganisms transmission,if Radiographers performthe hands hygienization before and after their use,...
Personal information and conflict of interest
T. C. P. L. Guerreiro; Lisboa/PT - nothing to disclose L. P. V. Ribeiro; Parchal/PT - nothing to disclose A. F. Abrantes; Faro/PT - nothing to disclose S. Rodrigues; Faro/PT - nothing to disclose R. Raposo; Faro/PT - nothing to disclose F. Soares; Faro/PT - nothing to disclose R. P. P. Almeida; Faro/PT - nothing to disclose H. S. Ponte; Lisboa/PT - nothing to disclose
Tatiana Guerreiro, Radiographer in Imaging Centre, Hospital da Luz- Lisbon, Portugal. E-mail:
[email protected]
Luís Ribeiro (PhD), Professor in the Medical...
References
Heggendornn, L., Gomes, S., Silva, N., Varges, R., & Póvoa, H. (2016). Epidemiological Profile And Antimicrobial Susceptibility Of Microorganisms Isolated From Nosocomial Infections. Revista Saúde e Meio Ambiente – RESMA, 2 (1), 26-47.
Direção-Geral de Saúde. Programa Nacional de Prevenção e Controlo da Infeção Associada aos Cuidadosde Saúde. 2007.
Crofton, C., & Foley, S. (2017). An investigation of mobile phone use in the radiology department and the success of an awareness campaign at reducing the associated nosocomial infection risks.
Direção-Geral de Saúde. Orientação de Boa...