Learning objectives
To review the multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI) findings of granulomatous prostatitis (GP).
To discuss and compare granulomatous prostatitis as a radiologic mimicker of prostate adenocarcinoma.
To share our experience on mp-MRI, in patients with biopsy-proven GP.
Background
Patients, who have clinical and laboratory findings suspicious for prostate cancer, routinely undergo mp-MRI instead of biopsy. In these patients, various anatomical structures and benign pathologies include prostatitis, thickening of the surgical capsule, post-biopsy hemorrhageand GP may cause a false-positive result on mp-MRI. GP is one of the best mimickers of prostate cancer(1).
GP is a rare, inflammatory condition that can mimic prostate cancer both clinically and radiologically(2). Oppenheimer et al. (3) reported the incidence of GP is 0,36% in a series of 25.000 men...
Findings and procedure details
MRI features of GP
GP lesions tend to originate from the peripheral zone and may be diffuse, nodular or occasionally multifocal(6).
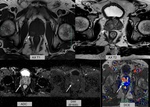
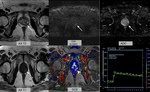
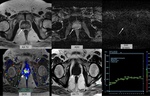
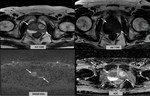
•OnT2 weighted images(T2WI); GP lesions appear hypointense and occasionally can cause capsular irregularity and/or capsular bulging(Fig. 1) which are suggestive of extracapsular extension (1,7).
•On diffusion-weighted images (DWI);GP lesions may show hyperintensity on high b-value diffusion images and low apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values consistent with impeded diffusion, similar to that of prostate cancer (1,7). It is supposed that impeded diffusion findings on DWI...
Conclusion
As discussed above, it is still challenging to distinguish GP from prostate cancer based on radiologic findings.
Lesions that have similar appearance with prostate cancer on mp-MRI but hyperintense on T1WI, GP should be kept in mind in the differential diagnosis.
It is important for the radiologist to consider the possibility of GP in patients who have predisposing risk factors like intravesical BCG immunotherapy, TUR-P or prostate biopsy history.
Personal information and conflict of interest
S. Durmaz; Istanbul/TR - Author at Saglik Bilimleri University Sisli Hamidiye Etfal Research and Training Hospital
B. Coskun; Istanbul/TR - Author at American Hospital
T. Gümüs; Istanbul/TR - Author at Koc University Hospital
M. Vural; Istanbul/TR - Author at American Hospital
References
Lee SM, Wolfe K, Acher P, Liyanage SH. Multiparametric MRI appearances of primary granulomatous prostatitis. Br J Radiol. 2019 Jun;92(1098):20180075.doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180075. Epub 2019 Apr 9. PubMed PMID: 30964700; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6592093
Logan JK, Walton-Diaz A, Rais-Bahrami S, Merino MJ, Turkbey B, Choyke PL,Pinto PA. Changes observed in multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging characteristics correlate with histopathological development of chronic granulomatous prostatitis after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014 Mar-Apr;38(2):274-6. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e3182aac58a. PubMed PMID: 24637671; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3995030.
Oppenheimer JR, Kahane...