Type:
Educational Exhibit
Keywords:
Anatomy, Computer applications, eHealth, CT, Experimental, Image manipulation / Reconstruction, CAD, Computer Applications-3D, Surgery, Cancer, Education and training, Multidisciplinary cancer care
Authors:
A. Ivančić, V. Kopačin
DOI:
10.26044/ecr2024/C-10959
Background
Advances in computer and diagnostic imaging technologies enable the surgical treatment of more complex cases, reducing surgery times and improving patient outcomes. However, these advances also leave surgeons sometimes dependent on advanced visualization techniques.
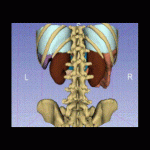
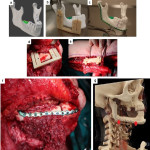
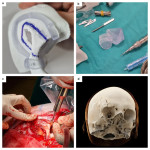
Until recently, radiologists had a limited toolkit, primarily consisting of maximum intensity projections (MIP), multiplanar reconstructions (MPR), and volume rendering techniques (VRT). Today, the field boasts sophisticated anatomy representation methods used in various clinical and educational scenarios. These include the cinematic rendering technique (CRT), extended reality (XR) encompassing both virtual (VR) and augmented (AR) reality, and three-dimensional (3D) printing.
Innovative visualization techniques serve as robust imaging technology, empowering radiologists and healthcare professionals to swiftly and accurately pinpoint major medical issues within complex scans.