Learning objectives
•Anatomy of ventricular system,
hemodynamic flow pattern of CSF en-route from its production to absorption
•Discuss various pathological causes that alters the hemodynamic flow pattern of CSF and the differential causes to be considered depending on the level of flow obstruction
•Role of imaging in diagnosis,
treatment and follow up of patients with hydrocephalus.
Background
Materials and Methods:
Retrospective analysis of 60 patients during the period 2011 to 2015 ,
presented with clinical and morphological findings suggestive of hydrocephalus where various imaging modalities was utilised to assess CSF flow dynamics in diagnosis and follow up.
Findings and procedure detail:
Role of different modalities like neurosonography (NSG),
CT,
MRI,
phase contrast-MRI (PC-MRI),
3D- heavily T2W MRI ,
Diffusion weighted imaging in identifying/localising the pathological cause of hydrocephalus and associated secondary changes .
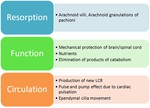
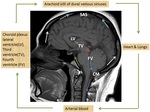
Physiology of CSF production & circulation:
Normal Cerebrospinal fluid...
Findings and procedure details
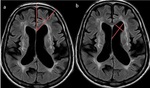
Types of hydrocephalus:
Communicating Unimpeded flow ofCSF from the ventricular system into the subarachnoid space,
impeded absorption at arachnoid villi (1-a)Obstruction to CSF absorption
Meningitis
Meningo-encephalitis
Intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH)
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis
(1-b) Without obstruction to CSF absorption
Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
Choroid plexus papilloma
2. Non-communicating
Impedence to flow of CSF in the path of ventricles.
DD for Foramen of monro obstruction
DD for 3rd ventricular obstruction
Colloid cyst
Craniopharyngioma
Craniopharyngioma
Hypothalamo-chiasmatic glioma - Pilocytic astrocytoma
Pituitary macroadenoma
Supratentorial and infratentorial extraventricular tumors...
Conclusion
• Imaging plays an inevitable role in assessing the CSF flow dynamics; aid in differentiating the type of hydrocephalus & to direct corrective manangement and follow up.
• In certain cases,
diffusion imaging in detecting periventricular interstitial oedema has been found to be superior to CT/MRI in accessing treatment response and sometimes in aiding diagnosis in equivocal clinical features.
•PC-MRI and /or 3D MRI are simple techniques that aid in assessing the physiology of CSF flow and to determine the level of obstruction.
Personal information
Dr Anirudh Nair,
MBBS MD
Specialist Radiologist,
Kerala Institute of Medical Science,
India .
Email:
[email protected]
References
Kahlon B,
Annertz M,
Stahlberg F,
Rehncrona S.
Is aqueductal stroke volume,
measured with cine phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging scans useful in predicting outcome of shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus?.Neurosurgery.
2007 Jan.
60(1):124-9; discussion 129-30.
Hattingen E,
Jurcoane A,
Melber J,
Blasel S,
Zanella FE,
Neumann-Haefelin T.
Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with adult chronic idiopathic hydrocephalus.Neurosurgery.
2010 May.
66(5):917-24.
Chmielowski K,
Podgorski JK,
Twarkowski P,
Pietrzykowski J,
Szalus N.
Radionuclide cisternography in the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Pol Merkur Lekarski.
2004...