Learning objectives
The objective of this study is to enumerate the normal cerebral venous anatomy along with some anatomic variants which may contribute significantly to misdiagnosis of common pathological conditions, particularly in non-contrast flow dependent MR venography techniques.
Background
The intracranial veins, unlike the systemic veins, do not follow their arterial counterparts and thus differ in their drainage territory from the arteries. Developmentally, the superficial and deep venous system has distinct embryology.Variations in cerebral venous anatomy is a rule rather than an exception. These variations must be kept in mind while evaluating a scanforpathologies like cerebral venous sinus thrombosis(CVT) or assessment of their patency in tumours encasing the venous sinuses1, 2.
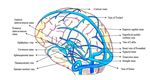
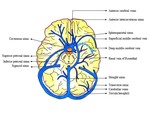
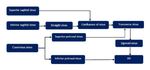
Normal venous anatomy3: The intracranial venous system has two major components, the dural...
Findings and procedure details
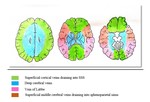
We have reviewed phase-contrast venography and post-contrast 3D –T1 spoiled gradient echo images of 60 patients who came to our institute with a wide spectrum of neurological symptoms. We have described a spectrum of normal as well as variant venous anatomy along with common pitfalls of venous sinus imaging.
Anomalies:
1. Anomalies of the transverse sinus (Fig. 6):
· Most common venous sinus to have anatomic variation, unilateral hypoplasia being the most common variation3.
·Right-sided hypoplasia is more common in females.
·Left-sided hypoplasiaequally seen in...
Conclusion
Variant sinus anatomy is often mistaken as sinus pathology thus increasing the burden of extensive unnecessary investigations.TS flow gap predominantly in the non-dominant one is a common occurrence in MRV. Small sinus size, slow or complex flow pattern, faulty image acquisition plane may all contribute to a false-positive diagnosis of CVT.
Sound knowledge about such variations in addition to an overview of potential imaging pitfalls is of utmost importance in tailoring the imaging protocol and reducing misdiagnosis.
Personal information and conflict of interest
S. Mahal; Jodhpur/IN - nothing to disclose S. Tiwari; Jodhpur, RAJASTHAN/IN - nothing to disclose T. Yadav; 110029/IN - nothing to disclose P. S. Khera; Jodhpur/IN - nothing to disclose
References
1. Mattle HP, Wentz KU, Edelman RR, Wallner B, Finn JP, Barnes P, Atkinson DJ, Kleefield J, Hoogewoud HM. Cerebral venography with MR. Radiology. 1991 Feb;178(2):453-8.
2. Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, McCully FJ, Theobald MR, Heiserman JE. Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2000 Jan 1;21(1):74-8.
3. Osborn AG, Hedlund GL, Salzman KL. Osborn's brain: imaging, pathology, and anatomy. Salt Lake City: Amirsys; 2013.
4. Ahmed MS, Imtiaz S, Shazlee MK, Ali M, Iqbal J, Usman...