Purpose
With the widespread use of imaging tests, the frequency of thyroid nodule identification has also increased. Thyroid nodules are very common in the whole population and are detected by ultrasonography in 50-60% of the population [1].
Ultrasonography currently is the best available method for the findings of nodules and its main purpose is to differentiate benign nodules from those at risk of malignancy and requiring ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) to make a definitive diagnosis and decide about the necessity of surgical intervention.
Thyroid Imaging...
Methods and materials
A prospective study in which thyroid ultrasound and FNA biopsy results of 176 patients from Clinical University Hospital and two private clinics were analyzed.
IBM SPSS software, 22.0 version (IBM Corm., Armonk, N.Y., USA), MS Excel 2010 software, and MedCalc Software Ltd 19.2.1 version (Mariakerke, Belgium) was used to analyze statistical data and create graphs. The statistical significance level of this study was assumed to be p-value < 0.05.
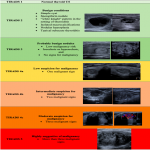
[Fig 1]
Ultrasonographic malignancy signs: markedly hypoechoic, irregular borders, macrocalcifications, taller than wide shape (AP>LL), specific...
Results
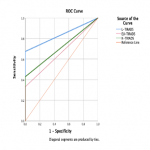
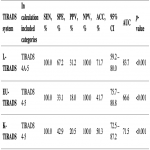
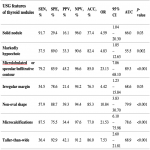
176 patients with 187 nodules, from which 151 female and 25 male were included in the study. 135 nodules (72.19%) were benign, 7 nodules (3.74%) were suspicious of malignancy, 17 nodules (9.09%) were malignant, and 14 nodules (7.49%) were non-diagnostic cytologically according to the Bethesda system. All TIRADS systems showed high sensitivity–100%. However, L-TIRADS is more accurate (71.7%) and with a better AUC (83.7%) compared to the EU-TIRADS (ACC=41.7%; AUC=66.6%) and K-TIRADS (ACC=50.3%; AUC=71.5%) (Table 1, Figure 2).
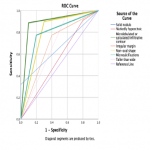
[Fig 4]
[Fig 2]
There are multiple...
Conclusion
A statistically significant difference of TIRADS systems performance has been defined: L-TIRADS (modified K-TIRADS) represents higher accuracy and a better AUC - 81.8% un 88.8%. EU-TIRADS and K-TIRADS show higher sensitivity – 95.8% and 91.7%, respectively. Microlobulated or spiculated/infiltrative contour has been shown to be an ultrasonographic malignancy feature with the highest sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy - 79.2%, 85.9%, and 85.0% (OR=23.13; p<0.001), as well as with a better AUC– 89.3%.
Personal information and conflict of interest
N. M. Popova:
Owner: Speaker
P. Prieditis:
Author: Scientific manager, Thyroid nodules examination and FNA
M. M. M. Tirane:
Investigator: Thyroid nodules examination and FNA
V. Linovs:
Investigator: Thyroid nodules examination and FNA
M. Rauda:
Investigator: Thyroid nodules examination and FNA
K. Stepanovs:
Investigator: thyroid nodules examination and FNA
M. Radzina:
CEO: Advisory board, research support, consultant
References
Skowrońska, A., Milczarek-Banach, J., Wiechno, W., Chudziński, W., Żach, M., Mazurkiewicz, M., Miśkiewicz, P., Bednarczuk, T., 2018. Accuracy of the European Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (EU-TIRADS) in the valuation of thyroid nodule malignancy in reference to the post-surgery histological results. Pol. J. Radiol. 83, e579–e586. https://doi.org/10.5114/pjr.2018.81556
Kwak, J.Y., Han, K.H., Yoon, J.H., Moon, H.J., Son, E.J., Park, S.H., Jung, H.K., Choi, J.S., Kim, B.M., Kim, E.-K., 2011. Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System for US Features of Nodules: A Step in Establishing Better...