Learning objectives
Explain the current evidence-based recommendations regarding radiological diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis and its role in monitoring disease activity,
progression,
prevention of complications and treatment outcome.
Document the main radiological findings associated with axial spondyloarthritis in early and late-phases,
as well as related complications and management.
Background
Acronyms:
AS - ankylosing spondylitis; ASAS - Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society; BASRI - Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiographic Index; EULAR - European League Against Rheumatism; fat-sat - fat-saturation; mSASSS; PA - Postero-Anterior; RA - Rheumatoid Arthritis; RASSS - Radiographic Ankylosign Spondylitis Spine Score; SI - Sacro-Iliac; SpA - spondyloarthritis; SPARCC - SPondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada; STIR - Short Tau Inversion Recovery; WI - Weighted Image
Introduction:
Spondyloarthropaties are a group of chronic inflammatory disorders that affect the musculoskeletal system and share several common features,...
Imaging findings OR Procedure Details
In this section,
we show the main active and chronic changes of the sacro-iliac joint and spine in patients with different stages of SpA.
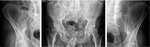
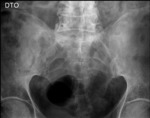
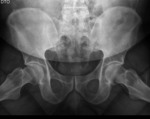
Sacro-iliac joint - Active inflammatory lesions
Inter-articular fluid collection – best seen on MRI due to the high sensitivy of T2WI sequences to fluid;T2WI with fat-saturation and STIR sequences are recommended;
Bone marrow edema / osteitis – may be found in other pathologies; in SpA,
affected areas are peri-articular and are frequently associated with other strucutral changes (e.g.
erosions); low-intensity signal...
Conclusion
There are currently specific recommendations with high level of evidence for diagnosis and management of axial spondyloarthritis.
While MRI appears to be fundamental in early-phase diagnosis and monitoring disease activity as well as response to treatment,
conventional radiography still has a role as a first approach in diagnosis and seems to be a valid method for assessing structural changes through scores such as the BASRI,
mSASSS and RASSS.
New semiquantitative methods are being developed,
targeted at MRI depicted changes,
which show promise and could be...
References
Ostergaard M,
Lambert RG.
Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis.
Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease (2012) 4(4) 301-311
Mandl P et al.
EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis in clinical practice.
Ann Rheum Dis (2015) 74: 1327-1339
Chaudhary SB,
et al.
Management of acute spinal fractures in ankylosing spondylitis.
ISRN Rheumatology (2011) 1-9
Canella C,
et al.
MRI in seronegative spondyloarthritis: imaging features and differential diagnosis in the spine and sacroiliac joints.
AJR (2013) 200: 149-157
Ramiro S,
et...